Journal of Social Systems and Policy Analysis
ISSN: 3068-5540 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
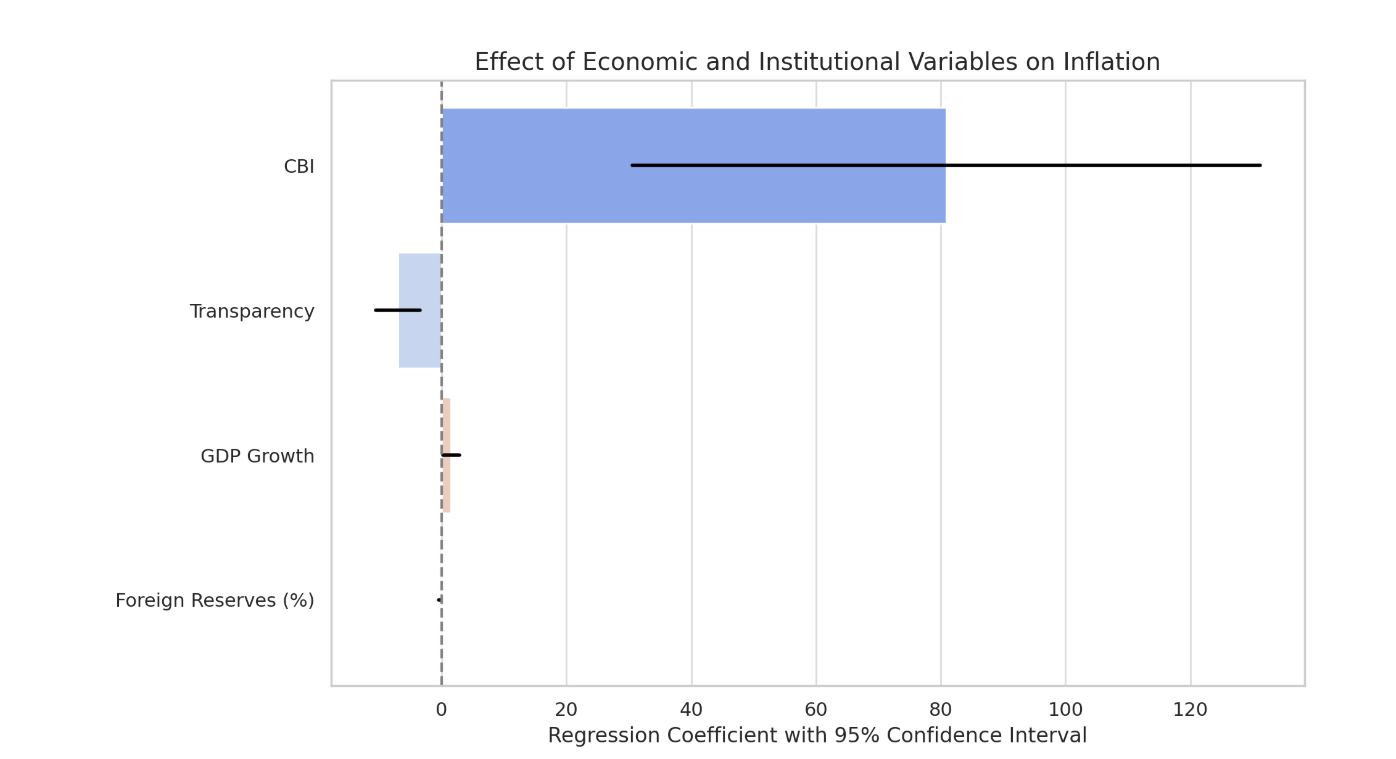
TY - JOUR AU - Song, Zhiming PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/17 TI - The Role of Central Bank Independence and Policy Transparency in Inflation Targeting: A Comparative Empirical Analysis of Five Countries JO - Journal of Social Systems and Policy Analysis T2 - Journal of Social Systems and Policy Analysis JF - Journal of Social Systems and Policy Analysis VL - 2 IS - 4 SP - 192 EP - 202 DO - 10.62762/JSSPA.2025.547905 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSSPA.2025.547905 KW - inflation targeting KW - central bank independence KW - policy transparency KW - monetary policy KW - international comparison KW - external shocks AB - Inflation targeting has become a cornerstone framework for contemporary monetary policy governance, yet its effectiveness varies significantly across countries. This study employs panel data from five countries—New Zealand, Canada, South Korea, Poland, and South Africa—over the period 2010 to 2020 to empirically examine the impact mechanisms of central bank independence and policy transparency on inflation dynamics. The findings indicate that institutional independence of central banks significantly contributes to curbing inflation levels, enhancing policy credibility and implementation stability. Meanwhile, policy transparency effectively reduces inflation volatility by stabilizing public expectations and strengthening market communication. Macroeconomic control variables, including the share of foreign exchange reserves and GDP growth rate, also play a moderating role in inflation fluctuations. Regression results reveal that the two core variables are statistically significant at the 1% level, with robust explanatory power of the model. Further analysis incorporating institutional heterogeneity demonstrates path-dependent differences in policy design and outcomes between developed and transition economies. Building on these findings, this paper proposes relevant policy recommendations that underscore the importance of strengthening central bank independence, enhancing policy transparency, improving exchange rate management frameworks, and promoting the gradual implementation of inflation targeting—particularly for emerging economies such as China. The conclusions provide theoretical support and empirical evidence for optimizing monetary policy institutions and macroeconomic regulation strategies. SN - 3068-5540 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Song2025The,
author = {Zhiming Song},
title = {The Role of Central Bank Independence and Policy Transparency in Inflation Targeting: A Comparative Empirical Analysis of Five Countries},
journal = {Journal of Social Systems and Policy Analysis},
year = {2025},
volume = {2},
number = {4},
pages = {192-202},
doi = {10.62762/JSSPA.2025.547905},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSSPA.2025.547905},
abstract = {Inflation targeting has become a cornerstone framework for contemporary monetary policy governance, yet its effectiveness varies significantly across countries. This study employs panel data from five countries—New Zealand, Canada, South Korea, Poland, and South Africa—over the period 2010 to 2020 to empirically examine the impact mechanisms of central bank independence and policy transparency on inflation dynamics. The findings indicate that institutional independence of central banks significantly contributes to curbing inflation levels, enhancing policy credibility and implementation stability. Meanwhile, policy transparency effectively reduces inflation volatility by stabilizing public expectations and strengthening market communication. Macroeconomic control variables, including the share of foreign exchange reserves and GDP growth rate, also play a moderating role in inflation fluctuations. Regression results reveal that the two core variables are statistically significant at the 1\% level, with robust explanatory power of the model. Further analysis incorporating institutional heterogeneity demonstrates path-dependent differences in policy design and outcomes between developed and transition economies. Building on these findings, this paper proposes relevant policy recommendations that underscore the importance of strengthening central bank independence, enhancing policy transparency, improving exchange rate management frameworks, and promoting the gradual implementation of inflation targeting—particularly for emerging economies such as China. The conclusions provide theoretical support and empirical evidence for optimizing monetary policy institutions and macroeconomic regulation strategies.},
keywords = {inflation targeting, central bank independence, policy transparency, monetary policy, international comparison, external shocks},
issn = {3068-5540},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/