Next-Generation Computing Systems and Technologies
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
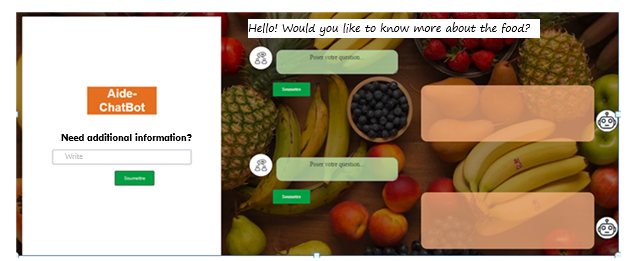
TY - JOUR AU - Rebai, Olfa AU - Charni, Maram AU - Aribi, Hiba Ben AU - Temessek, Malek Ben AU - Fattouch, Sami AU - Raboudi, Faten PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/07 TI - AI-driven Data Management of Traditional Tunisian Nutritional Dishes: A Cultural Heritage Conservation JO - Next-Generation Computing Systems and Technologies T2 - Next-Generation Computing Systems and Technologies JF - Next-Generation Computing Systems and Technologies VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 54 EP - 61 DO - 10.62762/NGCST.2025.714702 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/NGCST.2025.714702 KW - cultural heritage preservation KW - nutritional data systems KW - natural language processing KW - interactive platform KW - food heritage digitization AB - The potential loss of traditional Tunisian dishes threatens the sustainability of valuable cultural and nutritional traditions. To help preserve this rich heritage, a conversational AI system has been developed that employs advanced language processing and machine learning techniques to bring Tunisia’s culinary traditions to life in a digital space. Multilingual transformer models have been adapted to understand Tunisian dialects and combined with a detailed Food Heritage Knowledge Graph, allowing personalized, interactive access to authentic recipes and the stories behind them. A hybrid dialogue system operated by a chatbot has been implemented to ensure smooth, meaningful conversations that respect cultural sensitivities and build user trust and engagement.Despite challenges such as dialect diversity and limited data, it is demonstrated that modern AI can effectively capture and share complex cultural knowledge. Plans are underway to expand dialect support through federated learning and to improve contextual understanding with smarter memory models. Overall, this project highlights how technology and tradition can be connected through AI, supporting cultural preservation, promoting gastronomic tourism, and encouraging healthier eating habits in Tunisia. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Rebai2025AIdriven,
author = {Olfa Rebai and Maram Charni and Hiba Ben Aribi and Malek Ben Temessek and Sami Fattouch and Faten Raboudi},
title = {AI-driven Data Management of Traditional Tunisian Nutritional Dishes: A Cultural Heritage Conservation},
journal = {Next-Generation Computing Systems and Technologies},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {54-61},
doi = {10.62762/NGCST.2025.714702},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/NGCST.2025.714702},
abstract = {The potential loss of traditional Tunisian dishes threatens the sustainability of valuable cultural and nutritional traditions. To help preserve this rich heritage, a conversational AI system has been developed that employs advanced language processing and machine learning techniques to bring Tunisia’s culinary traditions to life in a digital space. Multilingual transformer models have been adapted to understand Tunisian dialects and combined with a detailed Food Heritage Knowledge Graph, allowing personalized, interactive access to authentic recipes and the stories behind them. A hybrid dialogue system operated by a chatbot has been implemented to ensure smooth, meaningful conversations that respect cultural sensitivities and build user trust and engagement.Despite challenges such as dialect diversity and limited data, it is demonstrated that modern AI can effectively capture and share complex cultural knowledge. Plans are underway to expand dialect support through federated learning and to improve contextual understanding with smarter memory models. Overall, this project highlights how technology and tradition can be connected through AI, supporting cultural preservation, promoting gastronomic tourism, and encouraging healthier eating habits in Tunisia.},
keywords = {cultural heritage preservation, nutritional data systems, natural language processing, interactive platform, food heritage digitization},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/