Abstract
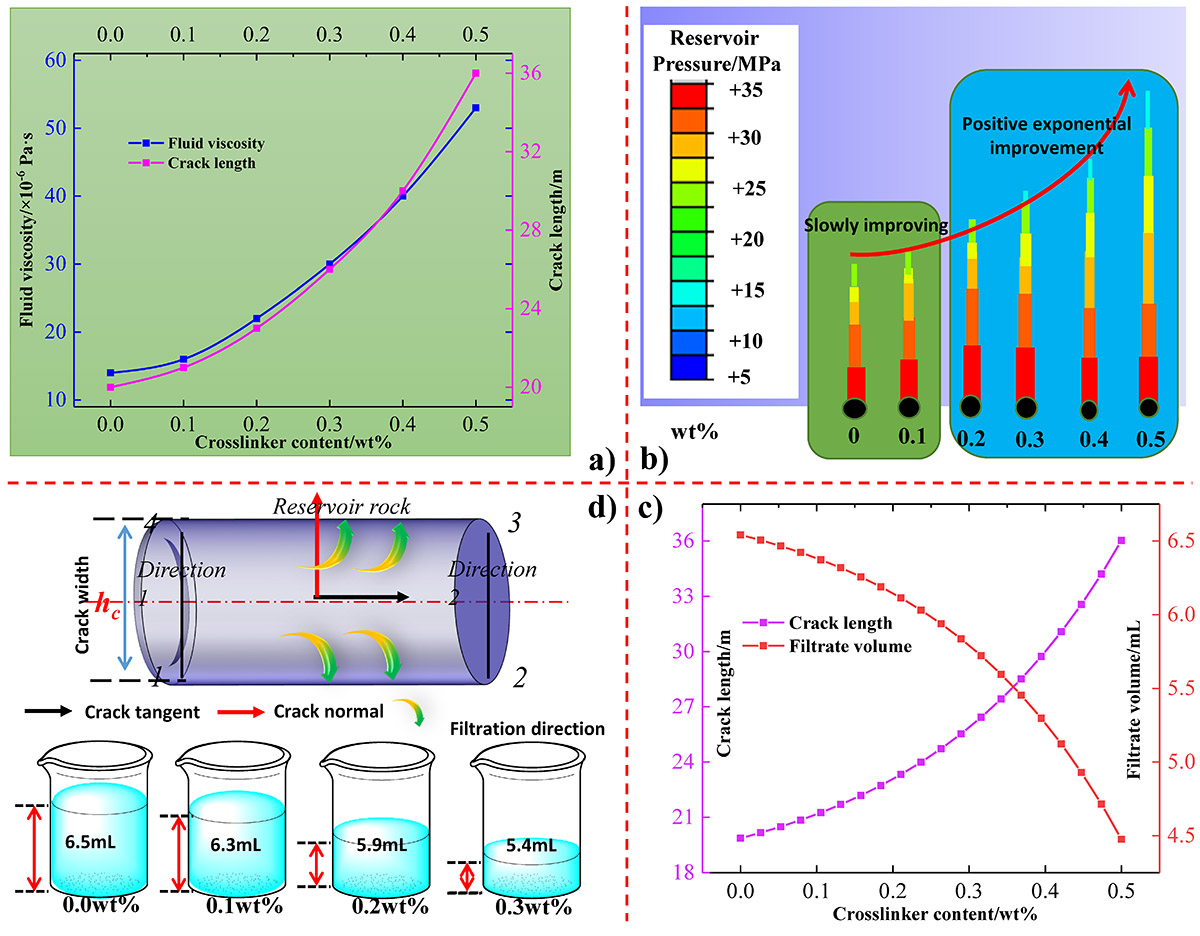
Low fracturing efficiency and high permeability filtration present substantial challenges during the fracturing development of coalbed methane (CBM), significantly hindering its efficient exploitation. In this study, a cross-linker featuring specific polar functional groups on its side chains was synthesized, and a multi-functional coupling evaluation apparatus was developed to systematically investigate the performance characteristics of water-based fracturing fluids. Furthermore, molecular dynamics simulations were employed to elucidate the microscopic mechanisms by which the modified cross-linkers and various external factors influence CBM extraction efficiency. The results indicated that the modified water-based fracturing fluid enhances fracture propagation and reduces fluid filtration into the reservoir. Increasing the concentration of the cross-linker (0wt% to 0.3wt%) improves both gas production efficiency and fracture expansion capacity (20m of crack length to 36m). Conversely, elevated reservoir temperatures (383K to 433K) markedly decrease gas recovery efficiency while significantly increasing fluid seepage (5.8ml to 7.5ml) and expansion capacity (26m of crack length to 42m). In contrast, higher reservoir pressure demonstrates an opposite trend by enhancing extraction efficiency and mitigating fluid filtration. The alteration of chemical bonding interactions between fluid molecules is identified as a key microscopic mechanism influencing CBM development, thereby offering a theoretical foundation for optimizing water-based fracturing strategies in low-permeability coal reservoirs.
Keywords
enhanced oil recovery
reservoir transformation
coalbed methane mining
water-based fracturing
low permeability reservoir
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Financial Assistance under Grant LBH-Z24245; in part by the Academic Success, the Introduction of Talent Research Start-up Program of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University under Grant XYB202003; in part by the Young Innovative Talents Project of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University under Grant ZRCQC202313.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Cao, L., Lv, M., Li, C., Sun, Q., Wu, M., Xu, C., & Dou, J. (2025). Effects of Crosslinking Agents and Reservoir Conditions on the Propagation of Fractures in Coal Reservoirs During Hydraulic Fracturing. Reservoir Science, 1(1), 36–51. https://doi.org/10.62762/RS.2025.494074
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 