Abstract
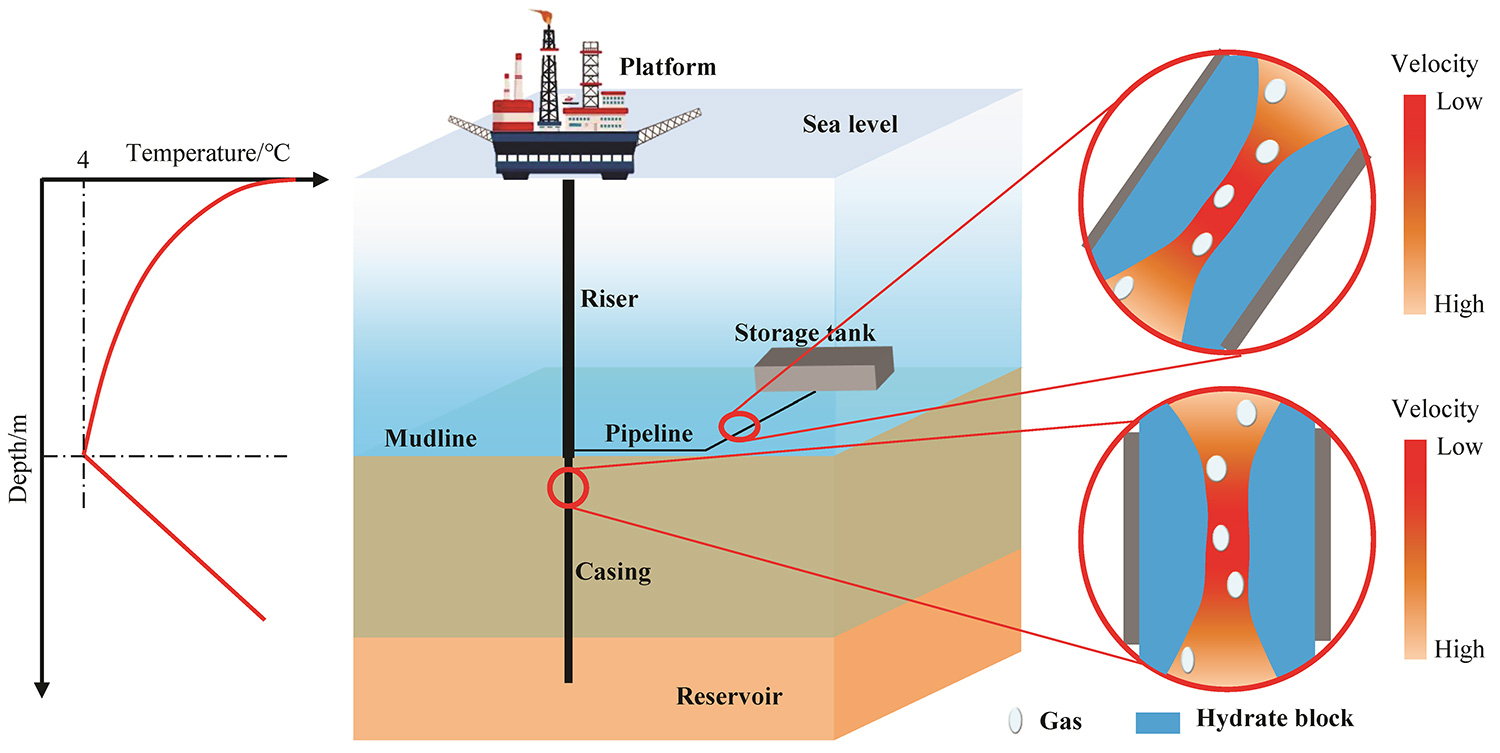
The low temperatures in the deepwater area are associated with a high risk of hydrate formation and flowline blockages in the wellbore and pipelines during the long-term development of gas reservoirs. The occurrence of this risk is required to be prevented and controlled to facilitate the safe and efficient development of offshore gas reservoirs. In this study, a numerical model was developed and solved to calculate the temperature and pressure distributions within wellbore and gathering system, and its applicability was evaluated. The comparison with experimental results verifies that the model is appropriate for predicting temperature and pressure distributions in the wellbore and gathering system during gas reservoir production. Simultaneously, the potential section for hydrate formation in the wellbore, flowline, and riser was examined by comparing the phase equilibrium pressure and actual pressure. The investigation results indicate that hydrate formation risks occurs in the wellbore, flowline, and riser after 10, 8, and 8 years of natural gas production, respectively. At these moments, the lengths of the hydrate formation risk sections in the wellbore, flowline, and riser are 49 m, 2500 m, and 9.8 m, respectively. Since then, the length of the hydrate formation risk section has increased with continued gas production operation. Finally, based on the phase equilibrium conditions associated with various methanol concentrations, the methanol injection concentration was optimized to eliminate the risk of hydrate formation. It is indicated by the investigation results that a methanol injection concentration of 7.5\% is required to eliminate the risk of hydrate formation in the wellbore and gathering system.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Li, M., Liu, J., & Xia, Y. (2025). Risk Prediction of Gas Hydrate Formation in the Wellbore and Subsea Gathering System of Deep-Water Turbidite Reservoirs: Case Analysis from the South China Sea. Reservoir Science, 1(1), 52–72. https://doi.org/10.62762/RS.2025.567907
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 