ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems
ISSN: 3070-2607 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
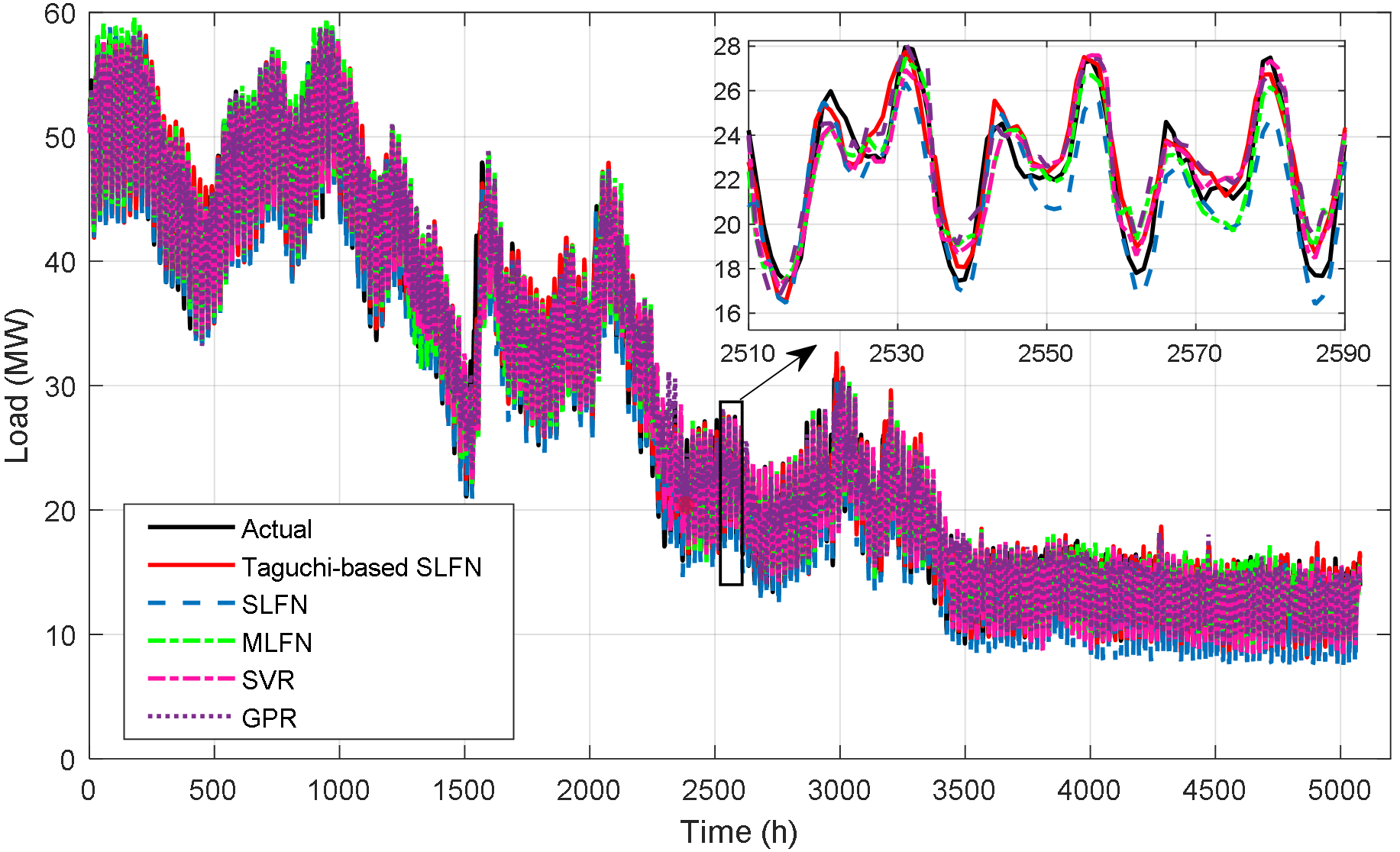
TY - JOUR AU - Milovanović, Miloš J. AU - Dragičević, Milorad M. AU - Krečković, Nebojša R. AU - Perović, Bojan D. PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/24 TI - Short-Term Load Forecasting with Taguchi-Optimized Single-Layer Feedforward Neural Networks: A MATLAB GUI JO - ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 70 EP - 81 DO - 10.62762/TEPNS.2025.295010 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TEPNS.2025.295010 KW - MATLAB GUI KW - neural networks KW - short-term load forecasting KW - taguchi method AB - This paper proposes a Taguchi-based optimization framework for short-term load forecasting (STLF) using single-layer feedforward neural networks (SLFNs). Although SLFNs are computationally efficient, their accuracy strongly depends on proper hyperparameter configuration, which is often selected through inefficient trial-and-error procedures. The proposed approach applies orthogonal arrays and signal-to-noise analysis to identify robust and reproducible SLFN settings. A MATLAB-based load forecasting interface is developed to support data preprocessing, model selection, parameter tuning, forecasting, and performance evaluation. The methodology is validated using real historical load and meteorological data from the distribution network supplying the municipalities of Kosovska Mitrovica, Zvečan, Leposavić, and Zubin Potok. The Taguchi-optimized SLFN achieves a mean absolute percentage error of 4.32% and a coefficient of determination of 0.991, outperforming all reference methods. More than one year of operational use confirms that forecasting errors consistently remain in the 3–5% range. These results demonstrate that lightweight neural architectures, when systematically optimized, provide a practical, accurate, and computationally efficient solution for real-world STLF applications. SN - 3070-2607 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Milovanovi2025ShortTerm,
author = {Miloš J. Milovanović and Milorad M. Dragičević and Nebojša R. Krečković and Bojan D. Perović},
title = {Short-Term Load Forecasting with Taguchi-Optimized Single-Layer Feedforward Neural Networks: A MATLAB GUI},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {70-81},
doi = {10.62762/TEPNS.2025.295010},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TEPNS.2025.295010},
abstract = {This paper proposes a Taguchi-based optimization framework for short-term load forecasting (STLF) using single-layer feedforward neural networks (SLFNs). Although SLFNs are computationally efficient, their accuracy strongly depends on proper hyperparameter configuration, which is often selected through inefficient trial-and-error procedures. The proposed approach applies orthogonal arrays and signal-to-noise analysis to identify robust and reproducible SLFN settings. A MATLAB-based load forecasting interface is developed to support data preprocessing, model selection, parameter tuning, forecasting, and performance evaluation. The methodology is validated using real historical load and meteorological data from the distribution network supplying the municipalities of Kosovska Mitrovica, Zvečan, Leposavić, and Zubin Potok. The Taguchi-optimized SLFN achieves a mean absolute percentage error of 4.32\% and a coefficient of determination of 0.991, outperforming all reference methods. More than one year of operational use confirms that forecasting errors consistently remain in the 3–5\% range. These results demonstrate that lightweight neural architectures, when systematically optimized, provide a practical, accurate, and computationally efficient solution for real-world STLF applications.},
keywords = {MATLAB GUI, neural networks, short-term load forecasting, taguchi method},
issn = {3070-2607},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems
ISSN: 3070-2607 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/