ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems
ISSN: 3070-2607 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
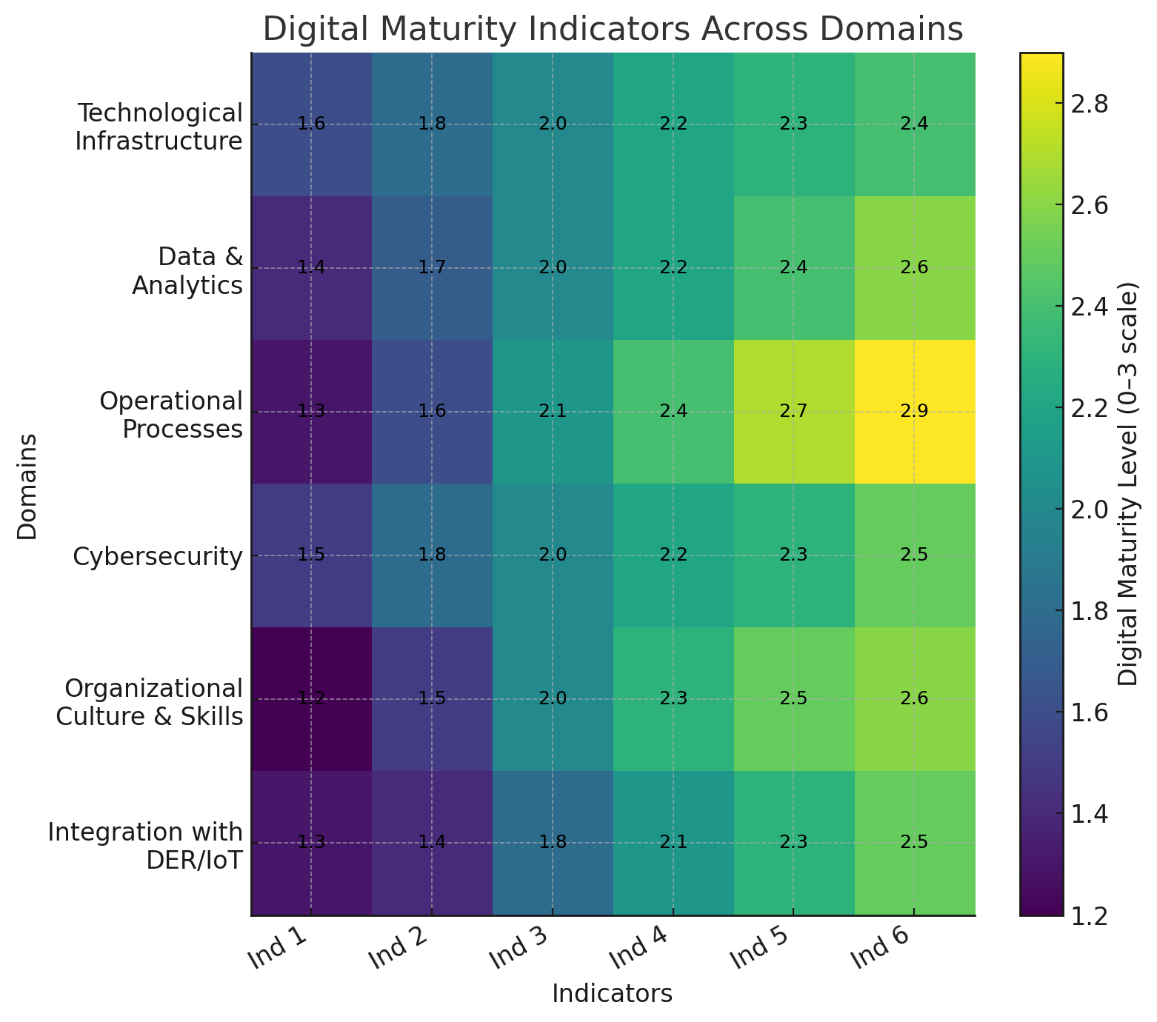
TY - JOUR AU - Stanchev, Plamen AU - Hinov, Nikolay AU - Zlatev, Zoran PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/30 TI - A Model for Assessing the Degree of Digitalization in Electric Power Networks JO - ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 93 EP - 108 DO - 10.62762/TEPNS.2025.524616 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TEPNS.2025.524616 KW - digitalization KW - power grid KW - maturity model KW - smart grid KW - assessment framework AB - The increasing integration of digital technologies into electric power networks has transformed traditional grids into complex cyber-physical systems. Yet, the level of digital maturity across operators remains uneven, lacking a unified assessment framework. This paper proposes a structured model for evaluating the degree of digitalization in power grids, integrating technological, organizational, and analytical dimensions. The model introduces six core domains, technological infrastructure, data and analytics, operational processes, cybersecurity, organizational culture, and distributed energy integration, each evaluated across four maturity levels. A weighted scoring system is used to compute a Digitalization Score Index (DSI), allowing quantitative comparison and benchmarking. The proposed model is tested through a case study involving a regional grid operator, demonstrating its capability to identify gaps and guide digital transformation strategies. Results show that such an approach enhances transparency, supports investment prioritization, and aligns network modernization with the principles of smart grid development. SN - 3070-2607 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Stanchev2025A,
author = {Plamen Stanchev and Nikolay Hinov and Zoran Zlatev},
title = {A Model for Assessing the Degree of Digitalization in Electric Power Networks},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {93-108},
doi = {10.62762/TEPNS.2025.524616},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TEPNS.2025.524616},
abstract = {The increasing integration of digital technologies into electric power networks has transformed traditional grids into complex cyber-physical systems. Yet, the level of digital maturity across operators remains uneven, lacking a unified assessment framework. This paper proposes a structured model for evaluating the degree of digitalization in power grids, integrating technological, organizational, and analytical dimensions. The model introduces six core domains, technological infrastructure, data and analytics, operational processes, cybersecurity, organizational culture, and distributed energy integration, each evaluated across four maturity levels. A weighted scoring system is used to compute a Digitalization Score Index (DSI), allowing quantitative comparison and benchmarking. The proposed model is tested through a case study involving a regional grid operator, demonstrating its capability to identify gaps and guide digital transformation strategies. Results show that such an approach enhances transparency, supports investment prioritization, and aligns network modernization with the principles of smart grid development.},
keywords = {digitalization, power grid, maturity model, smart grid, assessment framework},
issn = {3070-2607},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems
ISSN: 3070-2607 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/