ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
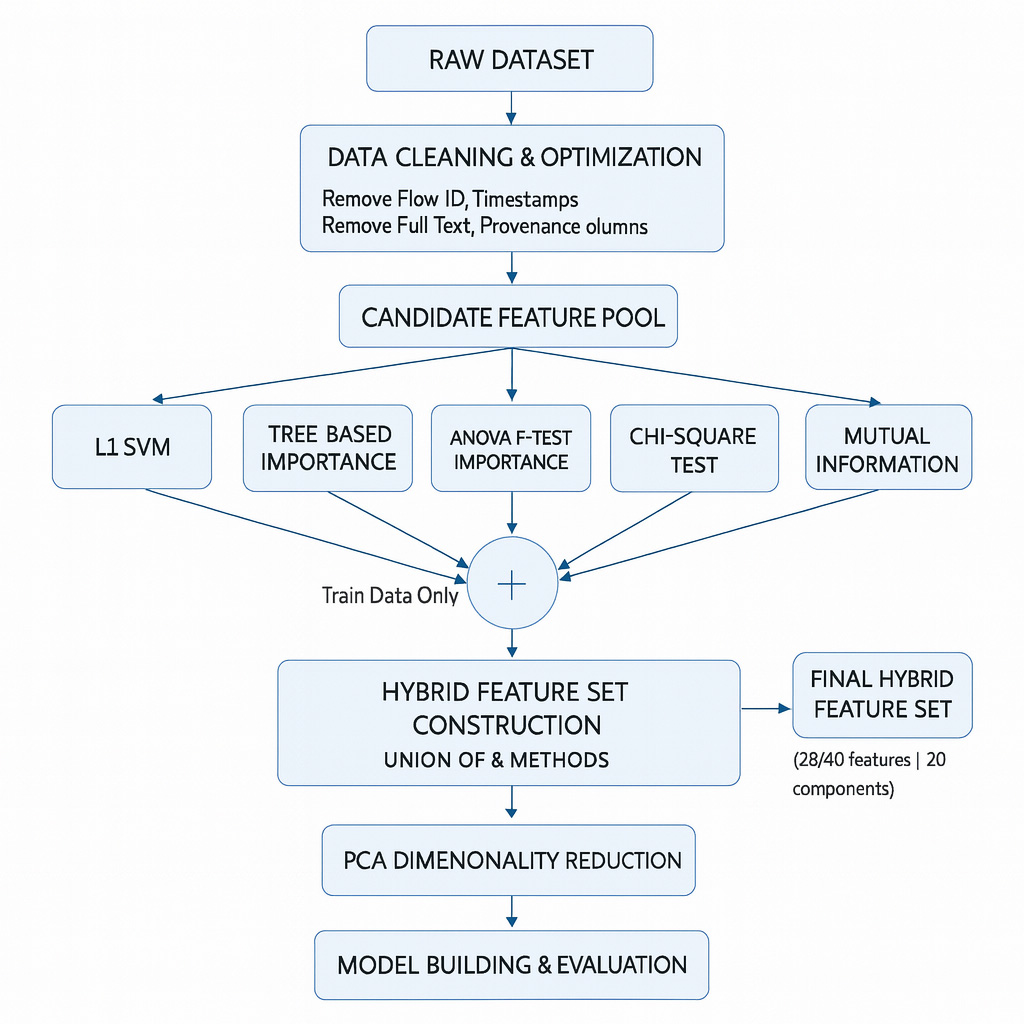
TY - JOUR AU - Ahmed, Nisar AU - Saleem, Gulshan AU - Naveed, Asim AU - Zaman, Muhammad Imran PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/11 TI - A Resource-Efficient Machine Learning Pipeline for DDoS Attack Detection: A Comparative Study on CIC-IDS2018 and CIC-DDoS2019 JO - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography T2 - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography JF - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 55 EP - 69 DO - 10.62762/TISC.2025.438083 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.438083 KW - distributed denial of service KW - DDoS detection KW - network intrusion detection KW - machine learning KW - deep learning KW - feature selection KW - class imbalance KW - CIC-IDS2018 KW - CIC-DDoS2019 AB - Distributed Denial of Service attacks remain a critical threat to modern networked systems due to their scale, diversity and evolving attack strategies. Although machine learning and deep learning techniques have been widely explored for DDoS detection, many existing studies rely on inconsistent preprocessing pipelines, single-dataset evaluations and limited reproducibility. This work proposes a unified and resource efficient detection framework that addresses these challenges through systematic data handling and transparent model evaluation. The proposed pipeline integrates data cleaning, memory optimization, class balancing and hybrid feature engineering that combines linear, tree-based, statistical and information-theoretic selection methods. Classical machine learning models and a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) are evaluated on two widely used benchmark datasets, CIC-IDS2018 and CIC-DDoS2019, under a leakage-free experimental protocol. Principal Component Analysis is further examined as an optional dimensionality reduction technique. Experimental results show that Random Forest and the CNN achieve strong and consistent performance across both datasets, with hybrid feature selection improving accuracy while reducing dimensionality. The findings demonstrate that careful preprocessing and feature engineering enable classical models to perform competitively with deep learning approaches while maintaining lower computational cost. The study emphasizes reproducibility, efficiency and practical deployability, providing a robust baseline for future DDoS detection research and real-world intrusion detection systems. SN - 3070-2429 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Ahmed2026A,
author = {Nisar Ahmed and Gulshan Saleem and Asim Naveed and Muhammad Imran Zaman},
title = {A Resource-Efficient Machine Learning Pipeline for DDoS Attack Detection: A Comparative Study on CIC-IDS2018 and CIC-DDoS2019},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {55-69},
doi = {10.62762/TISC.2025.438083},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.438083},
abstract = {Distributed Denial of Service attacks remain a critical threat to modern networked systems due to their scale, diversity and evolving attack strategies. Although machine learning and deep learning techniques have been widely explored for DDoS detection, many existing studies rely on inconsistent preprocessing pipelines, single-dataset evaluations and limited reproducibility. This work proposes a unified and resource efficient detection framework that addresses these challenges through systematic data handling and transparent model evaluation. The proposed pipeline integrates data cleaning, memory optimization, class balancing and hybrid feature engineering that combines linear, tree-based, statistical and information-theoretic selection methods. Classical machine learning models and a one-dimensional convolutional neural network (CNN) are evaluated on two widely used benchmark datasets, CIC-IDS2018 and CIC-DDoS2019, under a leakage-free experimental protocol. Principal Component Analysis is further examined as an optional dimensionality reduction technique. Experimental results show that Random Forest and the CNN achieve strong and consistent performance across both datasets, with hybrid feature selection improving accuracy while reducing dimensionality. The findings demonstrate that careful preprocessing and feature engineering enable classical models to perform competitively with deep learning approaches while maintaining lower computational cost. The study emphasizes reproducibility, efficiency and practical deployability, providing a robust baseline for future DDoS detection research and real-world intrusion detection systems.},
keywords = {distributed denial of service, DDoS detection, network intrusion detection, machine learning, deep learning, feature selection, class imbalance, CIC-IDS2018, CIC-DDoS2019},
issn = {3070-2429},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/