ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence
ISSN: 3068-7403 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
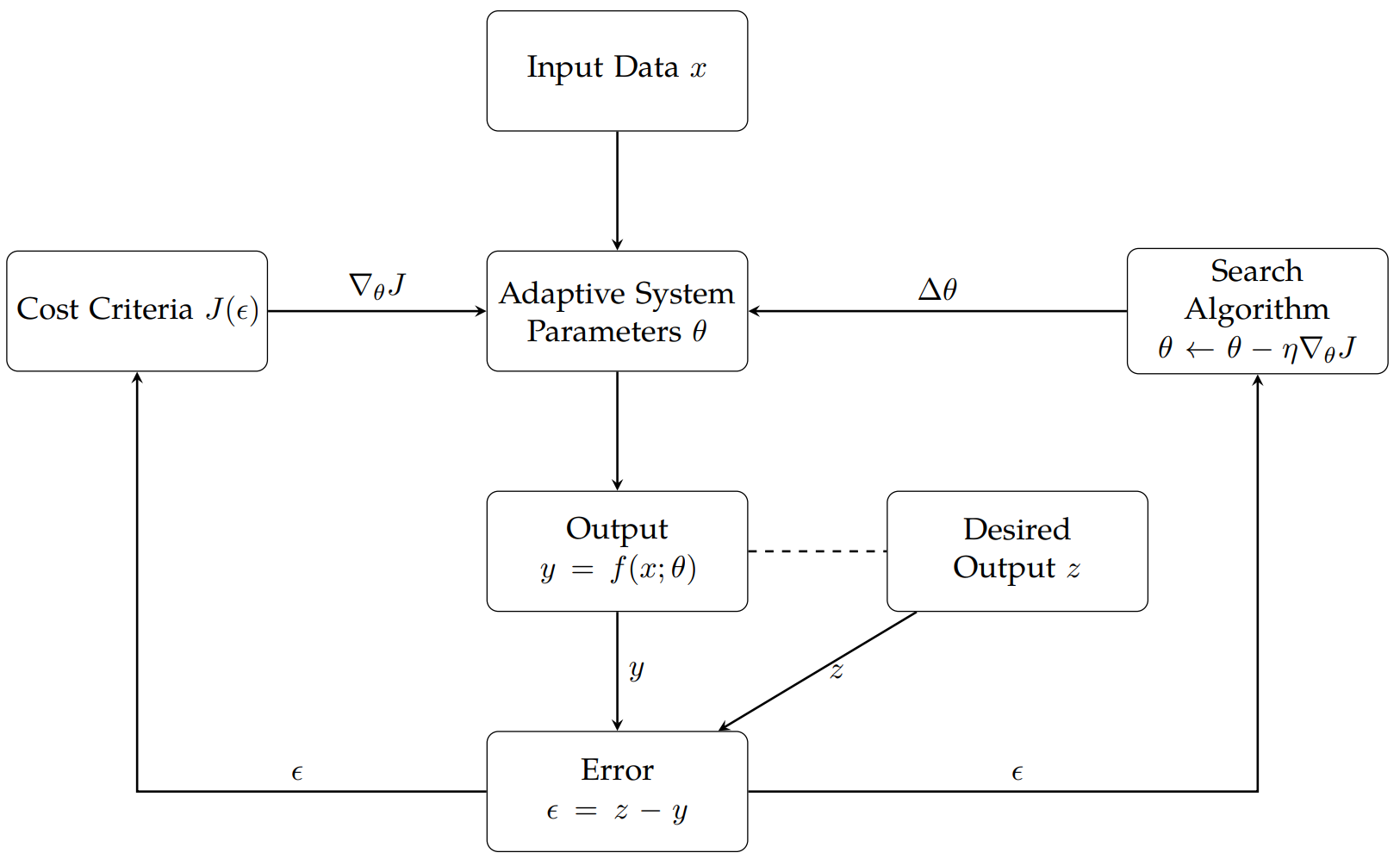
TY - JOUR AU - Kumar, Vijay AU - Saxena, Arti AU - Chawla, Leena PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/06 TI - Adaptive Learning Density Estimators for Tsallis Entropy and Kapur Entropy with Applications in System Training JO - ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence T2 - ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence JF - ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 12 EP - 27 DO - 10.62762/TMI.2025.317970 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TMI.2025.317970 KW - generalized entropies KW - adaptive learning KW - machine learning KW - kernel density estimation KW - information theoretic measures AB - Adaptation learning is a data-driven technique that gives instructions based on the experiences made during data analysis. It plays an integral role in providing engineering solutions based on specific needs. Researchers have used the second-order statistics criterion for decades to conceptualize the optimality criteria using Shannon and Renyis information-theoretic measures. Some gaps have been identified in this research work, and useful findings have been proved with generalized information-theoretic measures of Renyis as Tsallis entropy of order $\alpha$ and Kapur entropy of order $\alpha$ and type $\beta$ using the Parzen-Rosenblatt window. This work explored the problem of constructing kernel density estimators and their application in adaptive systems training. SN - 3068-7403 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Kumar2026Adaptive,
author = {Vijay Kumar and Arti Saxena and Leena Chawla},
title = {Adaptive Learning Density Estimators for Tsallis Entropy and Kapur Entropy with Applications in System Training},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {12-27},
doi = {10.62762/TMI.2025.317970},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TMI.2025.317970},
abstract = {Adaptation learning is a data-driven technique that gives instructions based on the experiences made during data analysis. It plays an integral role in providing engineering solutions based on specific needs. Researchers have used the second-order statistics criterion for decades to conceptualize the optimality criteria using Shannon and Renyis information-theoretic measures. Some gaps have been identified in this research work, and useful findings have been proved with generalized information-theoretic measures of Renyis as Tsallis entropy of order \$\alpha\$ and Kapur entropy of order \$\alpha\$ and type \$\beta\$ using the Parzen-Rosenblatt window. This work explored the problem of constructing kernel density estimators and their application in adaptive systems training.},
keywords = {generalized entropies, adaptive learning, machine learning, kernel density estimation, information theoretic measures},
issn = {3068-7403},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/