Abstract
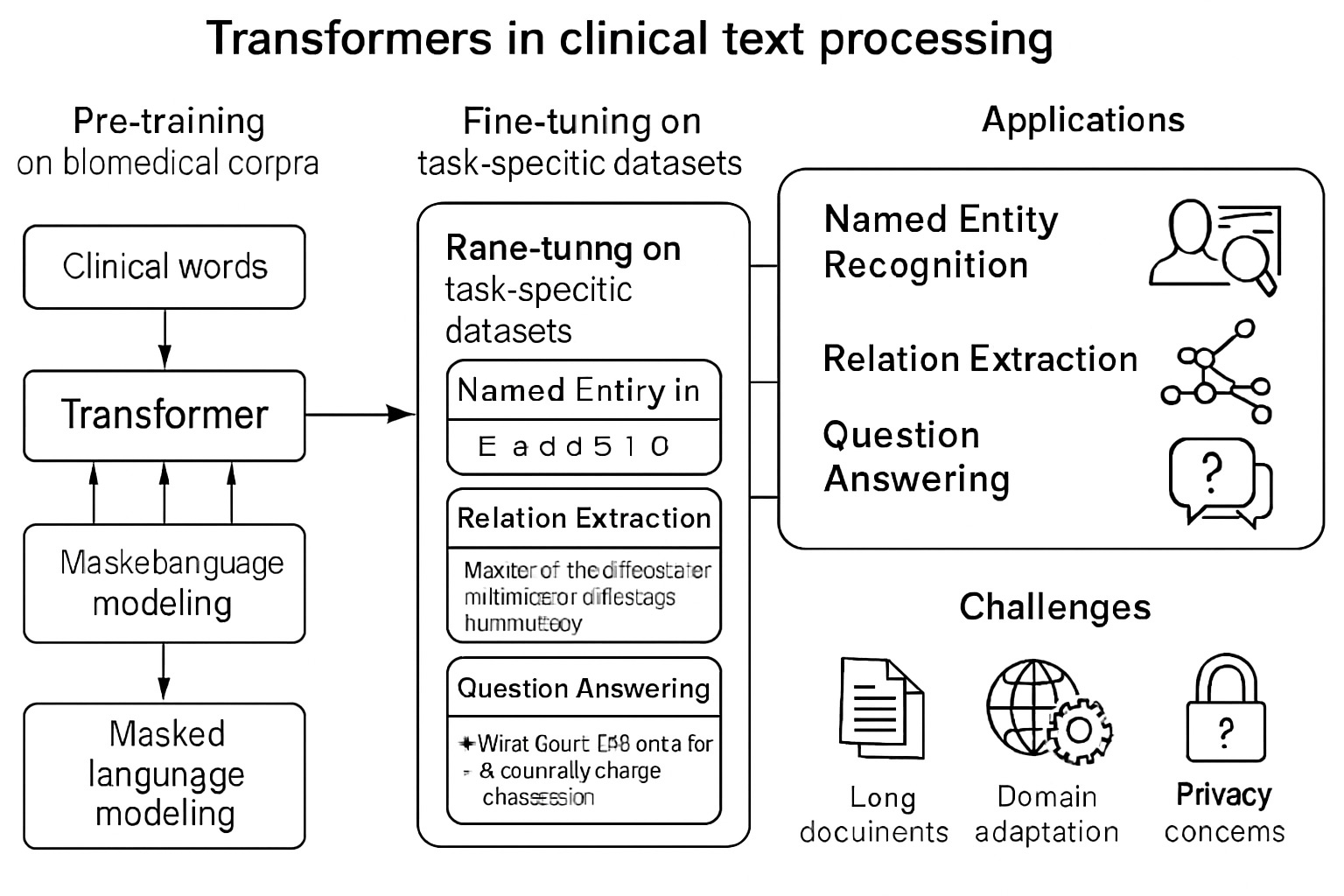
The healthcare sector has both opportunities and challenges as a result of the rapid expansion of unstructured clinical text data in electronic health records (EHRs). Physician notes, reports from radiologists, and summaries of discharge are examples of narrative medical documents from which relevant and actionable information can be extracted using clinical text analytics driven by Natural Language Processing (NLP). Named entity recognition, conceptual normalization, relation extraction, and temporal reasoning are just a few of the core methods and approaches in clinical natural language processing that are thoroughly covered in this paper. It covers cutting-edge deep learning models like BioBERT and ClinicalBERT as well as practical uses like clinical decision assistance, patient group identification, and adverse event detection. The paper also highlights future prospects including federated learning and multimodal integration, while addressing important issues in data privacy, annotation scarcity, and model interpretability. Clinical NLP has the potential to greatly improve patient care, biomedical research, and the effectiveness of the health system by converting free-text narratives into structured knowledge.
Keywords
clinical text
NLP
electronic health records (EHRs)
named entity recognition (NER)
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Kumar, A. (2025). Clinical Text Analytics: Techniques, Deep Learning Models, and the Future of Medical Text Analytics. ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence, 1(3), 148–165. https://doi.org/10.62762/TMI.2025.451731
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue