Abstract
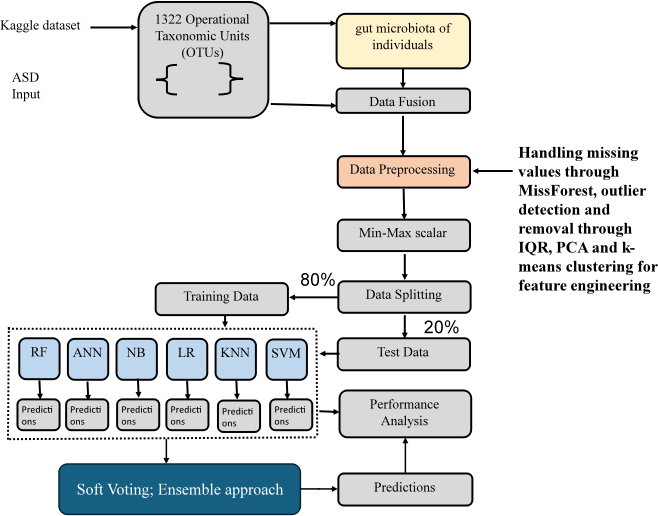
The Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnosis and detection in its initial stages is a more complex issue in the face of the wide-ranging, diverse nature and causes. Subsequent literature inclined towards a possible correlation of gut microbiome with ASD, and its disclosure presents a more promising attribute for imminent discovery conduits. The dataset on gut microbiome associated with ASD focuses specifically on the microbial compositions obtained through 16S rRNA sequencing. This study presents a novel method that integrates Artificial Intelligence employing various Machine Learning (ML) robust classifiers such that Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random Forest, k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Logistic Regression, and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), additionally PCA and k-means clustering is implemented for feature extraction to reveal important hidden patterns of ASD associated microbiomes from microbiome profiles. By integrating these model classifiers, the ensemble technique was developed to harness the strengths of each model, which enhances the dependability of the gut microbiome and offers a novel approach. The ensemble method suggested has an accuracy of 98.75%, a precision of 95.11%, a recall of 96.47% and an F1 score of 98.28% in the early determination of autism. The observational feature of this multifaceted approach not only enhances accuracy and precision but also provides a more complete picture of the role of autism spectrum disorders and eventually leads to the development of interventions and personalised approaches to these problems.
Keywords
autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
gut microbiome
artificial intelligence
machine learning
ensemble approach
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Singh, S., Aggarwal, S., Singh, A., & Sharma, A. (2025). Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Autism Detection via Gut Microbiome Analysis. ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence, 1(2), 90–102. https://doi.org/10.62762/TMI.2025.682666
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue