Digital Intelligence in Agriculture | Volume 1, Issue 2: 110-119, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/DIA.2025.914623
Abstract
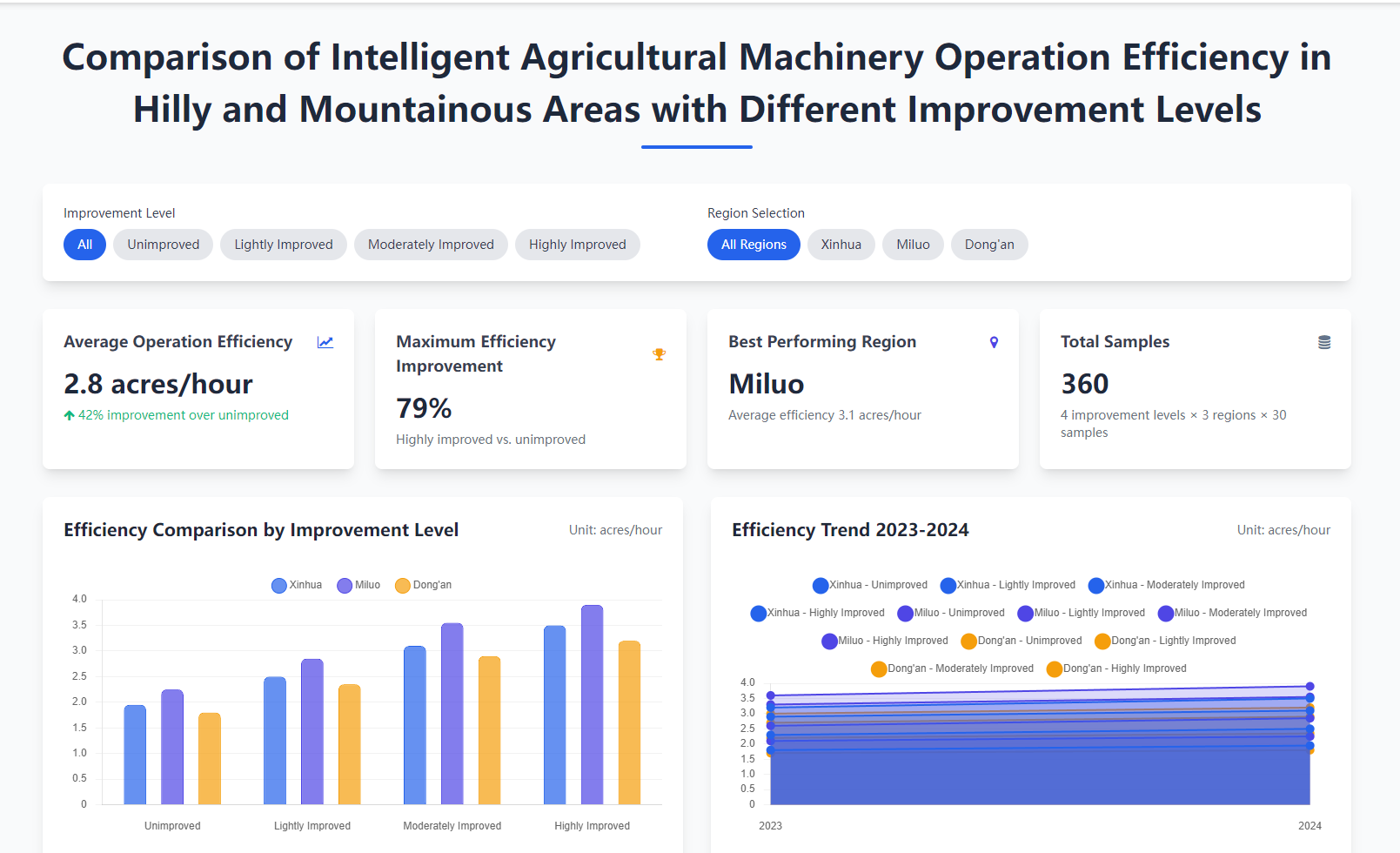
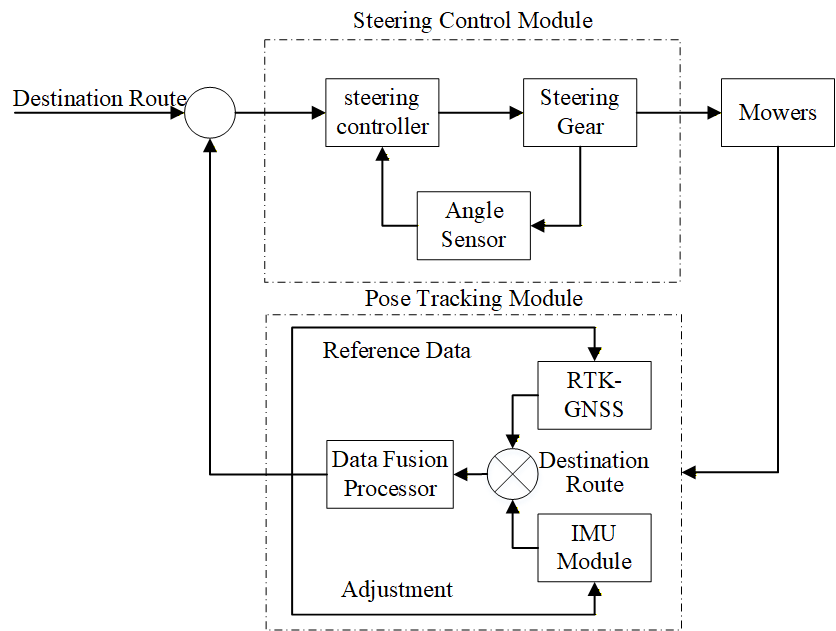
Hilly and mountainous areas account for 69% of China’s land area and undertake critical agricultural production tasks, but the poor adaptability of mainstream intelligent agricultural machinery and inefficient promotion models have become key bottlenecks restricting agricultural modernization. This study’s core innovation lies in constructing a ``four-dimensional integrated solution'' (equipment lightweight improvement - dynamic control optimization - hybrid sharing promotion - farmland mechanization-friendly transformation) and quantifying the coupling mechanism between topographic constraints and agricultural machinery performance. By introducing plot shape coefficient and slope volati... More >
Graphical Abstract