ICCK Journal of Software Engineering | Volume 1, Issue 2: 124-138, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JSE.2025.407864
Abstract
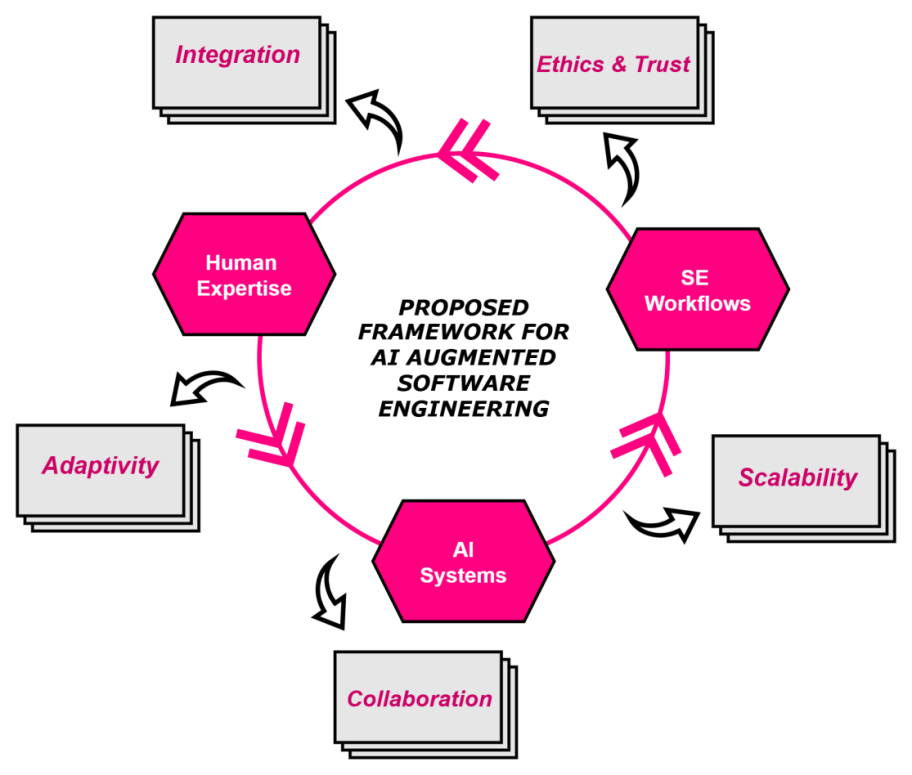
Software Engineering (SE) has traditionally relied on rule-based methods and human expertise to deliver reliable systems. As software systems grow more complex and the demand for intelligent and scalable solutions increases, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative approach. In particular, Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) play a central role in this shift. This paper proposes a theoretical framework for AI-augmented Software Engineering. It emphasizes the role of machine learning and deep learning across the entire software engineering lifecycle including requirement analysis, design, development, testing, maintenance, project management, and process improveme... More >
Graphical Abstract