Abstract
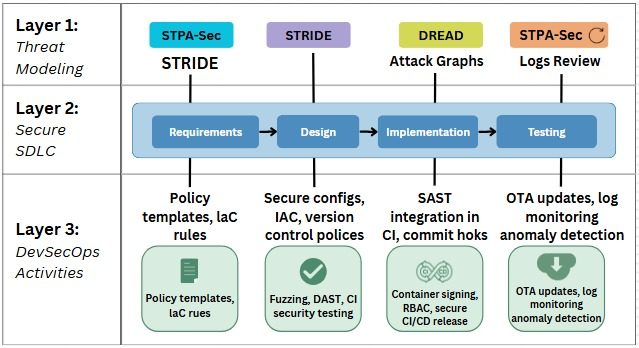
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is central to smart manufacturing, enabling real-time automation, data exchange, and system intelligence. However, the convergence of cyber-physical systems with legacy software and heterogeneous architectures introduces significant security challenges. This paper explores how software engineering principles can be strategically employed to enhance IIoT security by integrating threat modeling into the development lifecycle. In this study, we review classic models such as STRIDE, DREAD, and STPA-Sec, and evaluate their effectiveness when applied at various phases of the Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SSDLC). STRIDE focuses on classifying security threats, DREAD helps score the severity of risks, and STPA-Sec provides a safety-oriented approach to identifying unsafe control actions in IIoT environments. Additionally, we propose a secure development process to embed continuous security assurance during IIoT software deployment. This research highlights design-driven security patterns, model-driven engineering strategies, and secure API development best practices. This paper aims to support developers and architects in designing scalable and threat-aware IIoT systems through the alignment of software engineering with IIoT-specific threat vectors.
Keywords
industrial IoT
software engineering
threat modeling
secure software development lifecycle (SSDLC)
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Ali, M., Arif, H., Raza, A., & Nazir, M. (2025). Secure Software Engineering for Industrial IoT: Integrating Threat Modeling into the Development Lifecycle. ICCK Journal of Software Engineering, 1(2), 63–74. https://doi.org/10.62762/JSE.2025.729568
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 