ICCK Journal of Software Engineering | Volume 2, Issue 1: 11-29, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/JSE.2025.995217
Abstract
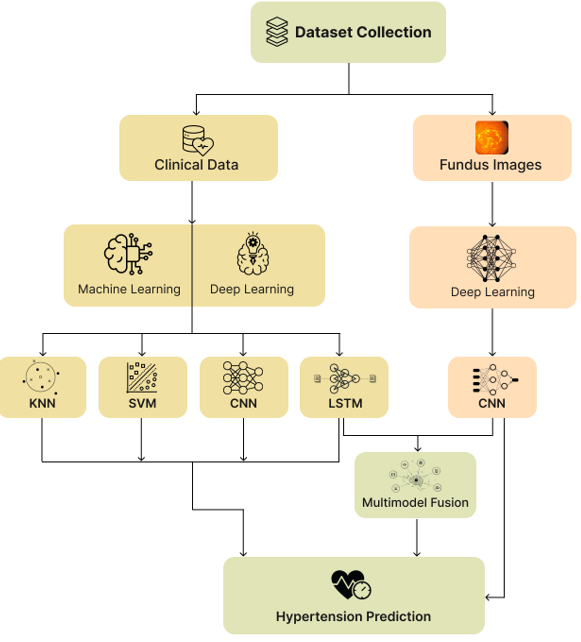
Hypertension, a life-threatening global health challenge, requires early detection to prevent severe cardiovascular complications. Fundus imaging reveals microvascular alterations, yet conventional diagnosis often misses subtle early changes. This study introduces a multimodal deep learning framework that integrates clinical data, fundus images, and demographic features to improve hypertension prediction. Unlike single-modality approaches, our method captures complementary risk factors from both structured and unstructured data. We evaluate machine learning and deep learning models on clinical data, confirming DL's superior accuracy. For fundus images alone, a CNN achieves 74.44% accuracy, h... More >
Graphical Abstract