ICCK Transactions on Swarm and Evolutionary Learning | Volume 1, Issue 2: 83-93, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TSEL.2025.913117
Abstract
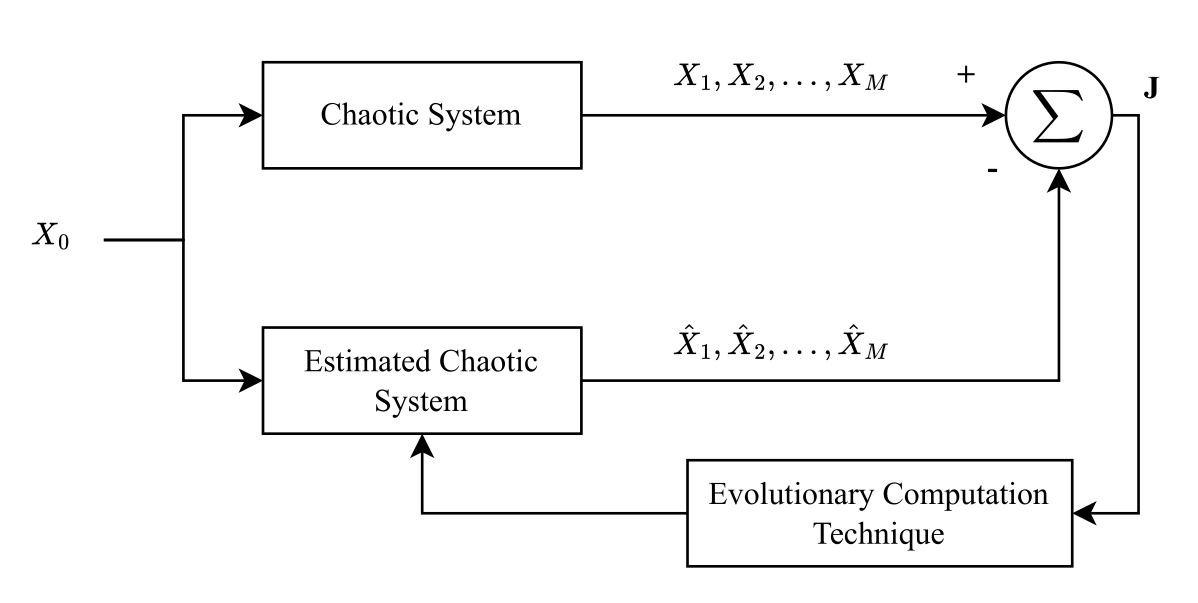
In recent years, Parameter Estimation (PE) has become a topic of growing interest due to its broad applications in science and engineering. An important application is the identification of Chaotic Systems (CS), which enables synchronization and control of chaotic behavior. However, the parameter estimation of CS is a highly nonlinear and multidimensional optimization problem where traditional approaches are often unsuitable. To overcome these limitations, Evolutionary Computation Techniques (ECT) have been widely adopted to tackle complex nonlinear optimization tasks. Recently, classical and modern ECT methods have been proposed for estimating the parameters of chaotic systems. However, mos... More >
Graphical Abstract