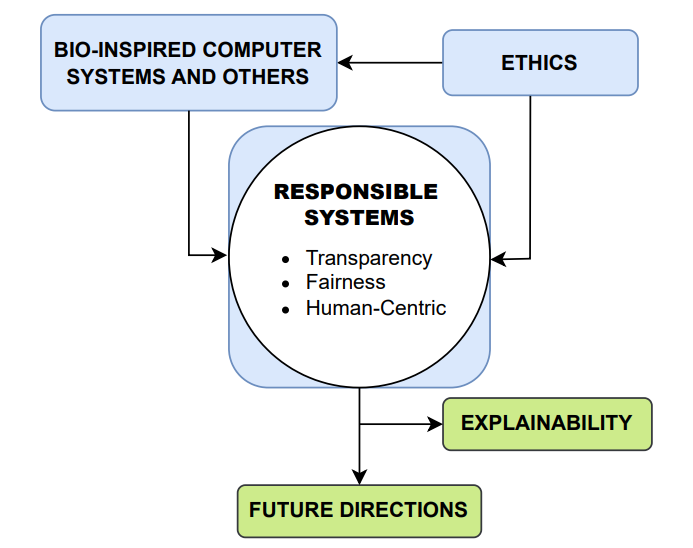
Abstract
Swarm and evolutionary computation topics has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in solving complex optimization problems across various scientific and engineering fields. However, as these methods are increasingly used in high-risk applications such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems, there is a growing need to address their ethical, interpretability, and social implications. This editorial outlines key guidelines for creating bio-inspired computing systems that are responsible and transparent, highlighting the fundamental role of ethics and explainability in shaping the future of evolutionary and swarm learning.
Keywords
swarm and evolutionary computation
explainable AI
responsible AI
computational ethics
human-centered AI
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Navarro-Velázquez, M. A. (2025). The Age of AI Responsibility: Towards Human-Centric and Ethical Swarm Intelligence. ICCK Transactions on Swarm and Evolutionary Learning, 1(1), 29–31. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSEL.2025.807182
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue