Abstract
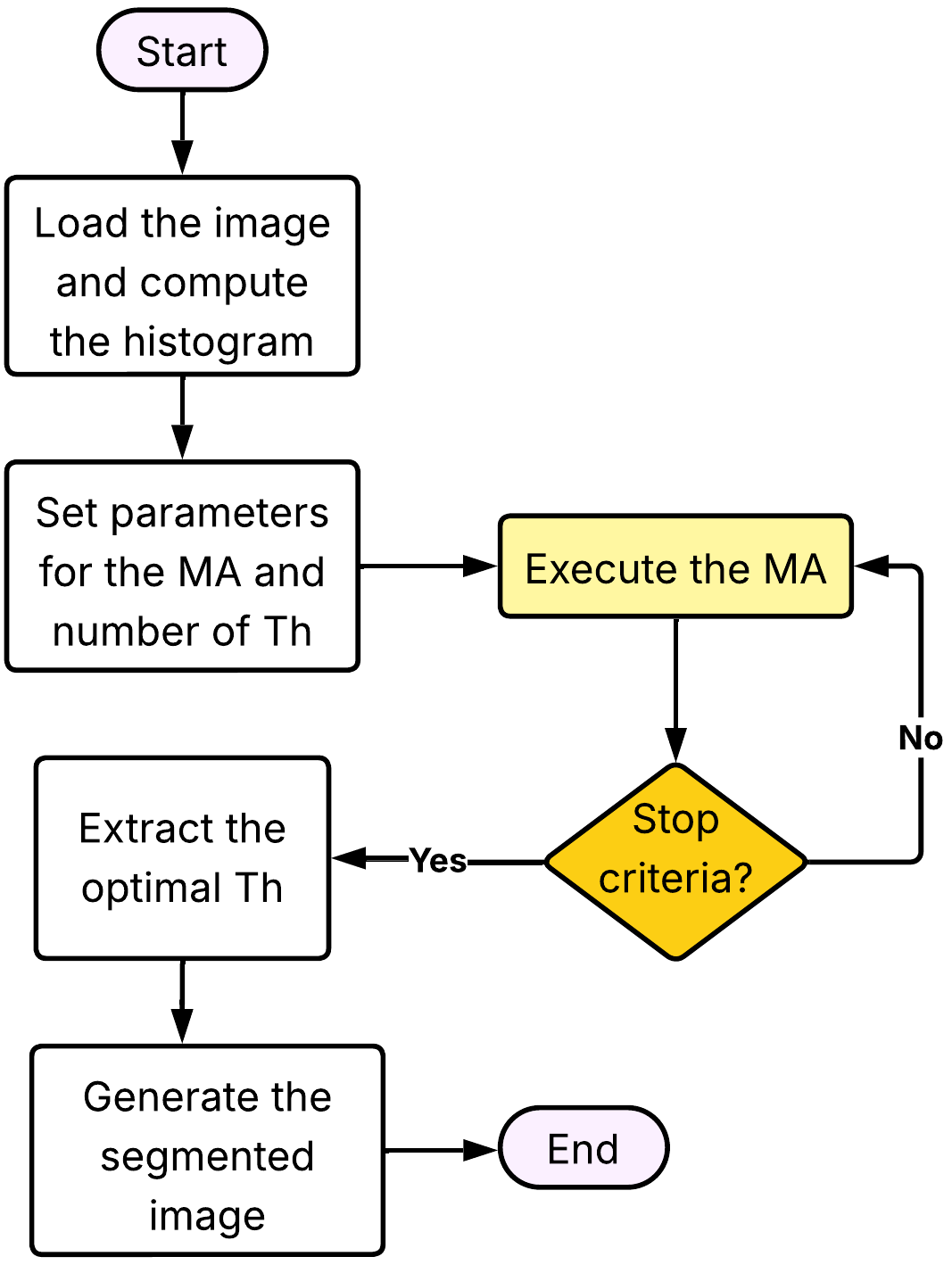
Metaheuristic Algorithms (MAs) are commonly used in the scope of digital image processing, in particular, image segmentation processes. This is evident in Multilevel Thresholding (MTH) methods, where the optimal threshold configuration must be found to produce high-quality segmented images. Minimum Cross-Entropy (MCE) is one of the most prominent techniques for MTH due to its simplicity and efficiency. This article proposes a comparison of recent MAs that have not yet been implemented for image segmentation. Six recently published MAs were implemented and tested on nine complicated images selected from the BSDS300 dataset. Analyzing the results reveals the best algorithm when MCE is used as the objective function. Central tendency indicators, such as Standard Deviation and mean, are also used to analyze the five threshold values. Additionally, three quality indicators used in processing images are analyzed: Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity (SSIM), and Feature Similarity (FSIM). The result of this analysis allows for the quality of the segmentation of each algorithm used in the comparison. The metrics with the highest values are indicative of the most effective algorithm in terms of segmentation performance.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Alvarez, O., Beltran, L. A., Casas-Ordaz, A., Ramos-Frutos, J., Navarro-Velázquez, M. A., Ramos-Soto, O., & Oliva, D. (2025). A Comparative Analysis of Recent Metaheuristic Algorithms for Image Segmentation Using the Minimum Cross-Entropy for Multilevel Thresholding. ICCK Transactions on Swarm and Evolutionary Learning, 1(2), 50–82. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSEL.2025.417356
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue