Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
ISSN: 3070-393X (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
TY - JOUR
AU - Jiao, Hui
AU - Meleshko, Sergey
PY - 2025
DA - 2025/11/26
TI - Analysis of a Pest-Natural Enemy Model with Time Delay in Impulsive Releasing Natural Enemy
JO - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
T2 - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
JF - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
VL - 1
IS - 1
SP - 20
EP - 28
DO - 10.62762/JMIA.2025.442174
UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JMIA.2025.442174
KW - pest-natural enemy model
KW - time delay
KW - impulsive releasing
KW - pest management
KW - pest-free
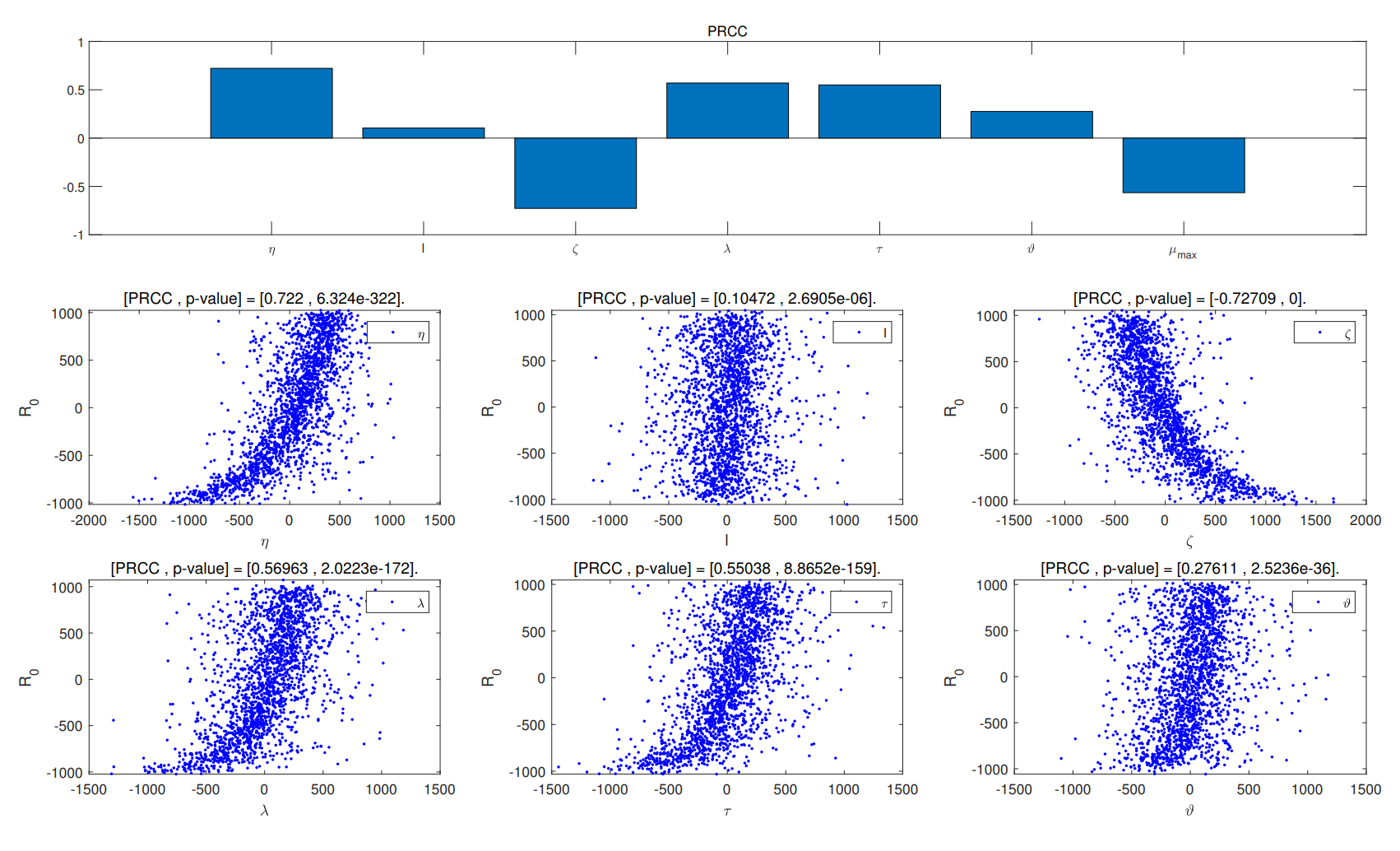
AB - Releasing amount of natural enemy generally depends on its population data, while impulsive releasing natural enemy usually brings about a time delay after the data is observed in the practical pest management. Therefore, it is very important for pest managers to assess the impact of the time delay in pest management. In this paper, we construct a pest-natural enemy model with time delay in impulsive releasing natural enemy. We prove that the pest-free periodic solution of model $(2.1)$ is globally attractive with $\eta \tau\frac{\zeta y^{\ast}(1-e^{-\lambda \tau})}{\lambda}$. Further influence of the time delay in impulsive releasing on dynamical behaviors of model $(2.1)$ is investigated by numerical simulations. Our results provide reliable tactics for pest management.
SN - 3070-393X
PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge
LA - English
ER -
@article{Jiao2025Analysis,
author = {Hui Jiao and Sergey Meleshko},
title = {Analysis of a Pest-Natural Enemy Model with Time Delay in Impulsive Releasing Natural Enemy},
journal = {Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {20-28},
doi = {10.62762/JMIA.2025.442174},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JMIA.2025.442174},
abstract = {Releasing amount of natural enemy generally depends on its population data, while impulsive releasing natural enemy usually brings about a time delay after the data is observed in the practical pest management. Therefore, it is very important for pest managers to assess the impact of the time delay in pest management. In this paper, we construct a pest-natural enemy model with time delay in impulsive releasing natural enemy. We prove that the pest-free periodic solution of model \$(2.1)\$ is globally attractive with \$\eta \tau\frac{\zeta y^{\ast}(1-e^{-\lambda \tau})}{\lambda}\$. Further influence of the time delay in impulsive releasing on dynamical behaviors of model \$(2.1)\$ is investigated by numerical simulations. Our results provide reliable tactics for pest management.},
keywords = {pest-natural enemy model, time delay, impulsive releasing, pest management, pest-free},
issn = {3070-393X},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
ISSN: 3070-393X (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/