Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
ISSN: 3070-393X (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
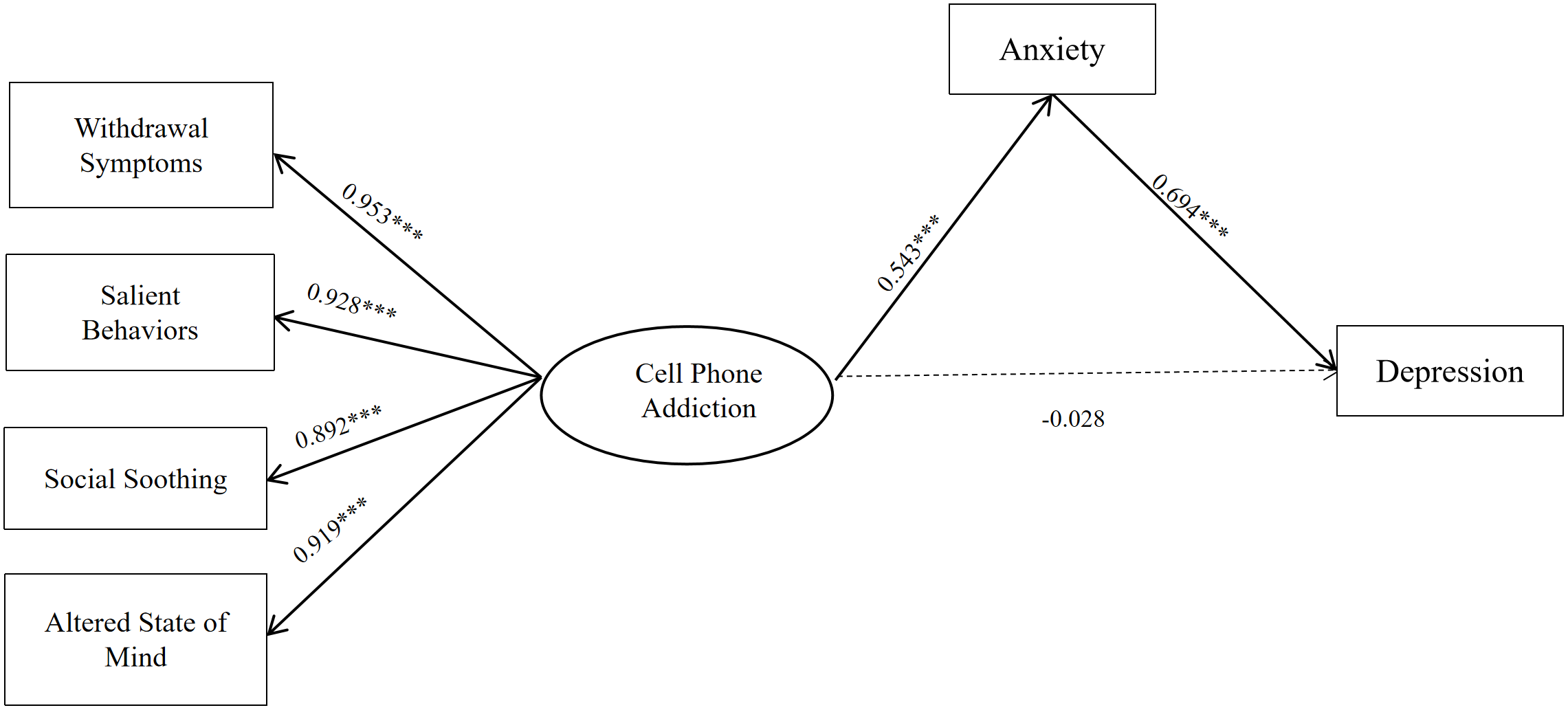
TY - JOUR AU - Deng, Haijun AU - He, Qun AU - Hua, Feiyan AU - Dai, Keyue AU - Tao, Lisha AU - Yao, Lan AU - Yang, Zhengfeng AU - Zhang, Quan AU - Jiao, Jianjun PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/28 TI - Modeling the Mediating Effect of Anxiety on Cell Phone Addiction and Depression Among College Students: A Structural Equation Analysis JO - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications T2 - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications JF - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 1 EP - 11 DO - 10.62762/JMIA.2025.883899 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JMIA.2025.883899 KW - cell phone addiction KW - anxiety KW - depression KW - mediating effect KW - structural equation AB - (1) Objective: This study aims to examine the relationships between college students' cell phone addiction, anxiety, and depression, and to explore the mediating role of anxiety in the association between cell phone addiction and depression. (2) Methods: Data were statistically analyzed using SPSS and AMOS. Independent samples t-tests and F-tests were employed to analyze differences in cell phone addiction (and its dimensions) across demographic variables. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to assess the relationships among cell phone addiction, anxiety, and depression. Structural equation modeling (SEM) via AMOS was used to validate the hypothetical model, and regression analysis combined with the bias-corrected percentile Bootstrap method was applied to test the mediating effect. (3) Results: College students' cell phone addiction showed significant differences by gender and grade. Their addiction characteristics were primarily reflected in prominent withdrawal symptoms, with a mean score of 16.64±5.40. Significant positive correlations were observed among cell phone addiction, anxiety, and depression (all p SN - 3070-393X PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Deng2026Modeling,
author = {Haijun Deng and Qun He and Feiyan Hua and Keyue Dai and Lisha Tao and Lan Yao and Zhengfeng Yang and Quan Zhang and Jianjun Jiao},
title = {Modeling the Mediating Effect of Anxiety on Cell Phone Addiction and Depression Among College Students: A Structural Equation Analysis},
journal = {Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {1-11},
doi = {10.62762/JMIA.2025.883899},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JMIA.2025.883899},
abstract = {(1) Objective: This study aims to examine the relationships between college students' cell phone addiction, anxiety, and depression, and to explore the mediating role of anxiety in the association between cell phone addiction and depression. (2) Methods: Data were statistically analyzed using SPSS and AMOS. Independent samples t-tests and F-tests were employed to analyze differences in cell phone addiction (and its dimensions) across demographic variables. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to assess the relationships among cell phone addiction, anxiety, and depression. Structural equation modeling (SEM) via AMOS was used to validate the hypothetical model, and regression analysis combined with the bias-corrected percentile Bootstrap method was applied to test the mediating effect. (3) Results: College students' cell phone addiction showed significant differences by gender and grade. Their addiction characteristics were primarily reflected in prominent withdrawal symptoms, with a mean score of 16.64±5.40. Significant positive correlations were observed among cell phone addiction, anxiety, and depression (all p},
keywords = {cell phone addiction, anxiety, depression, mediating effect, structural equation},
issn = {3070-393X},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
ISSN: 3070-393X (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/