Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing
ISSN: 3070-6424 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
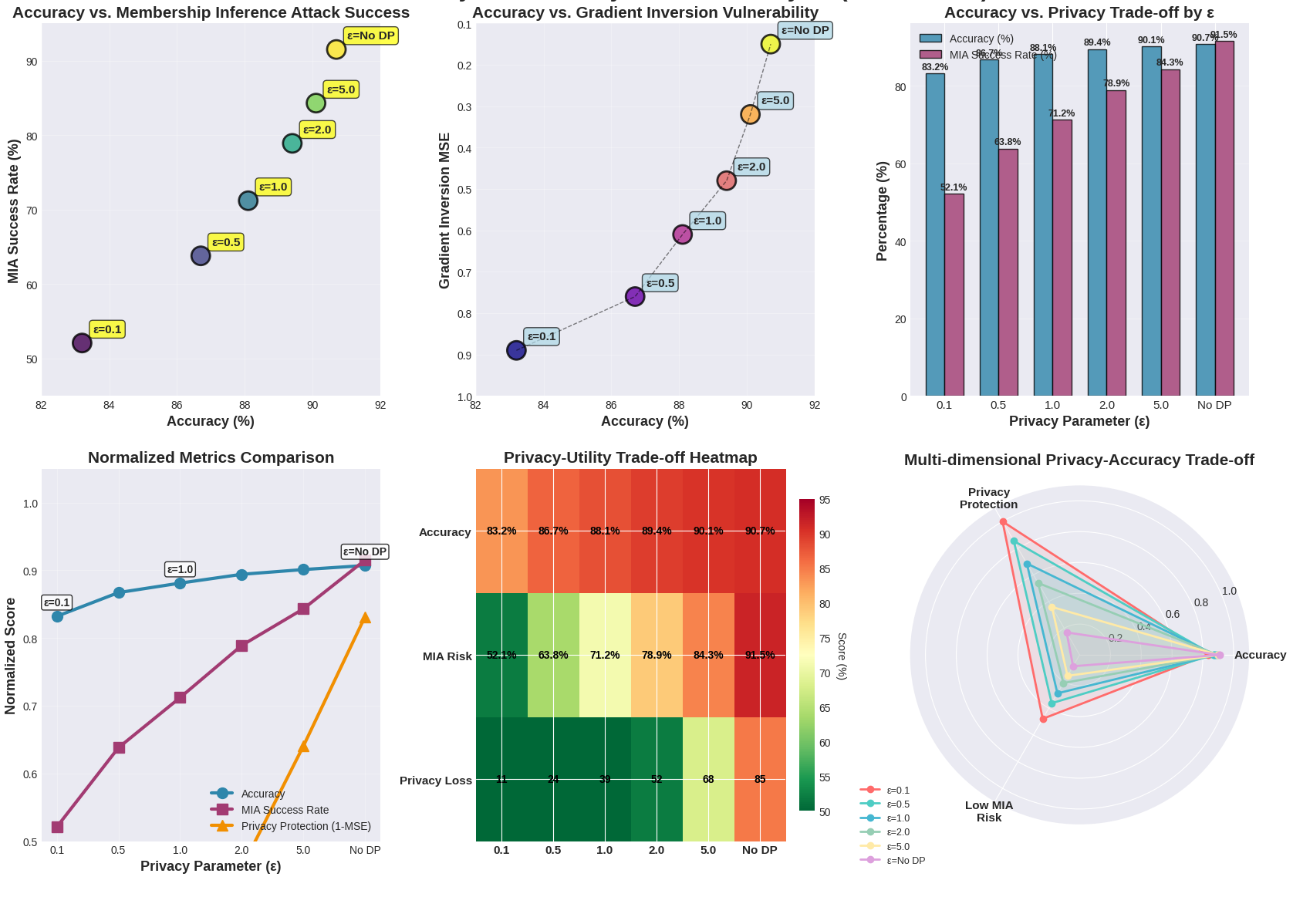
TY - JOUR AU - Alghamdi, Amro AU - Keshta, Ismail PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/28 TI - Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms and Enhancement Techniques for Federated Learning-Based Intrusion Detection Systems in IoT Smart Homes JO - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing T2 - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing JF - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 1 EP - 26 DO - 10.62762/JRSC.2025.761390 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRSC.2025.761390 KW - smart home security KW - internet of things (IoT) KW - intrusion detection system (IDS) KW - federated learning (FL) KW - blockchain KW - consensus mechanisms KW - privacy-preserving machine learning KW - decentralized trust KW - model poisoning KW - cyber security AB - The rapid proliferation of smart home IoT devices has introduced unprecedented cybersecurity vulnerabilities, necessitating scalable and privacy-preserving intrusion detection systems (IDS). Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising decentralized approach by training models locally without sharing raw data, but it remains susceptible to poisoning attacks and relies on a vulnerable central aggregator. This paper presents a novel blockchain-enhanced FL framework tailored for smart home IDS, integrating multiple consensus mechanisms—Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and Proof-of-Authority (PoA)—for the first time in this context. Our approach uniquely combines differential privacy (DP) and secure aggregation (SA) within a blockchain-managed workflow to mitigate gradient inversion and membership inference attacks while ensuring tamper-resistant, decentralized trust. Experimental evaluation using the N-BaIoT dataset demonstrates that the proposed system achieves up to 88.3% detection accuracy with manageable latency (~200 ms/round) and formal privacy guarantees ($\varepsilon$=1.0 DP). The framework introduces 52.8% system overhead compared to vanilla FL—a reasonable trade-off for enhanced security and privacy. This work establishes a robust, transparent, and scalable security infrastructure for smart homes, effectively addressing the limitations of both centralized and conventional FL-based IDS. SN - 3070-6424 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Alghamdi2026Blockchain,
author = {Amro Alghamdi and Ismail Keshta},
title = {Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms and Enhancement Techniques for Federated Learning-Based Intrusion Detection Systems in IoT Smart Homes},
journal = {Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {1-26},
doi = {10.62762/JRSC.2025.761390},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRSC.2025.761390},
abstract = {The rapid proliferation of smart home IoT devices has introduced unprecedented cybersecurity vulnerabilities, necessitating scalable and privacy-preserving intrusion detection systems (IDS). Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising decentralized approach by training models locally without sharing raw data, but it remains susceptible to poisoning attacks and relies on a vulnerable central aggregator. This paper presents a novel blockchain-enhanced FL framework tailored for smart home IDS, integrating multiple consensus mechanisms—Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and Proof-of-Authority (PoA)—for the first time in this context. Our approach uniquely combines differential privacy (DP) and secure aggregation (SA) within a blockchain-managed workflow to mitigate gradient inversion and membership inference attacks while ensuring tamper-resistant, decentralized trust. Experimental evaluation using the N-BaIoT dataset demonstrates that the proposed system achieves up to 88.3\% detection accuracy with manageable latency (~200 ms/round) and formal privacy guarantees (\$\varepsilon\$=1.0 DP). The framework introduces 52.8\% system overhead compared to vanilla FL—a reasonable trade-off for enhanced security and privacy. This work establishes a robust, transparent, and scalable security infrastructure for smart homes, effectively addressing the limitations of both centralized and conventional FL-based IDS.},
keywords = {smart home security, internet of things (IoT), intrusion detection system (IDS), federated learning (FL), blockchain, consensus mechanisms, privacy-preserving machine learning, decentralized trust, model poisoning, cyber security},
issn = {3070-6424},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/