Abstract
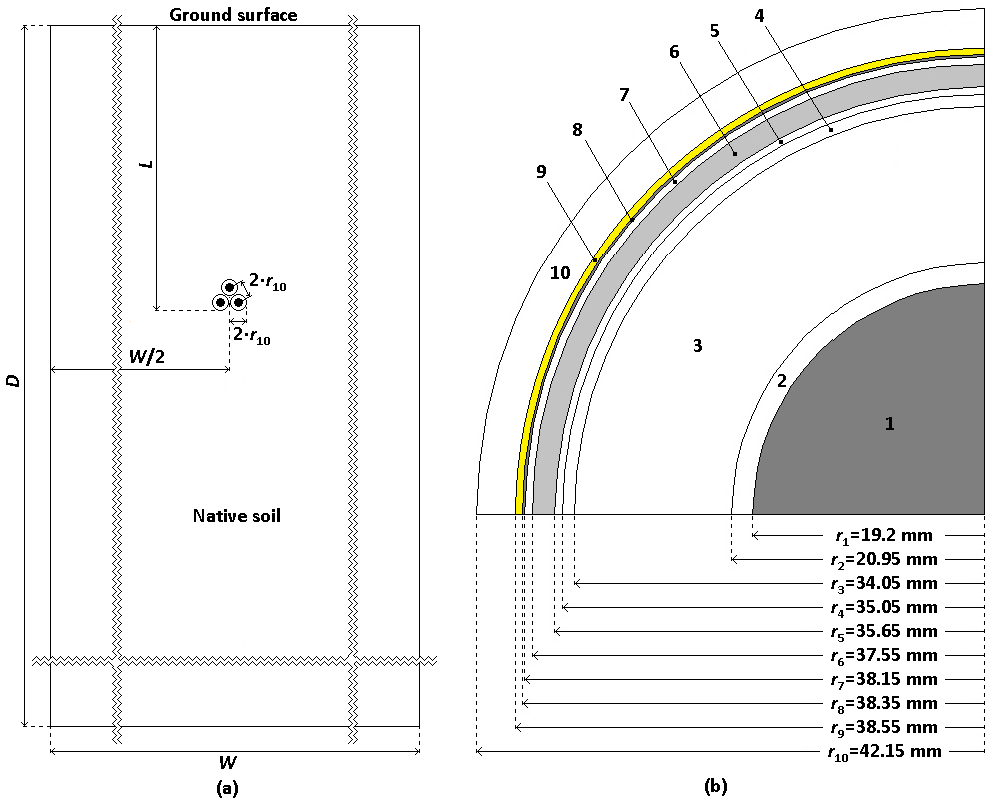
In the last decade, design engineers have been increasingly required to calculate the ampacities of cable lines using the finite element method (FEM) according to IEC TR 62095, especially for cases that cannot be solved analytically based on IEC 60287. In this regard, CIGRE Study Committee B1 noted in 2020 that there are many gaps in the technical report IEC TR 62095 and then published in 2025 a technical brochure. However, a certain number of those gaps still remained unaddressed. This paper proposes concrete solutions for addressing several gaps related to underground single-core power cables in trefoil formations. 110 kV single-core cables with cross-linked polyethylene insulation are considered, and FEM-based modeling is used for their steady-state thermal analysis. FEM-based models utilized here assume that the cables are installed directly in the dried-out soil, without cable bedding, under the most unfavorable ambient conditions. Appropriate analytical IEC-based models are used to verify the correctness of the proposed solutions. The ampacity obtained using the FEM differs from the corresponding IEC 60287-based value by only -0.263%, and the maximum conductor temperature deviations from the continuously permissible temperature are lower than 0.01 °C. The differences guarantee the reliability of FEM-based calculations.
Keywords
ampacity
finite element method (FEM)
power cable
steady-state thermal analysis
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was a part of the research conducted within the projects No. NIO 200132, NIO 200155 and NIO 200148 supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Klimenta, D., Sucurovic, M., & Tasic, D. (2025). Amendments to some IEC TR 62095 Recommendations for Underground Single-Core Power Cables in Trefoil Formation. ICCK Transactions on Electric Power Networks and Systems, 1(1), 38–49. https://doi.org/10.62762/TEPNS.2025.641725
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue