ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
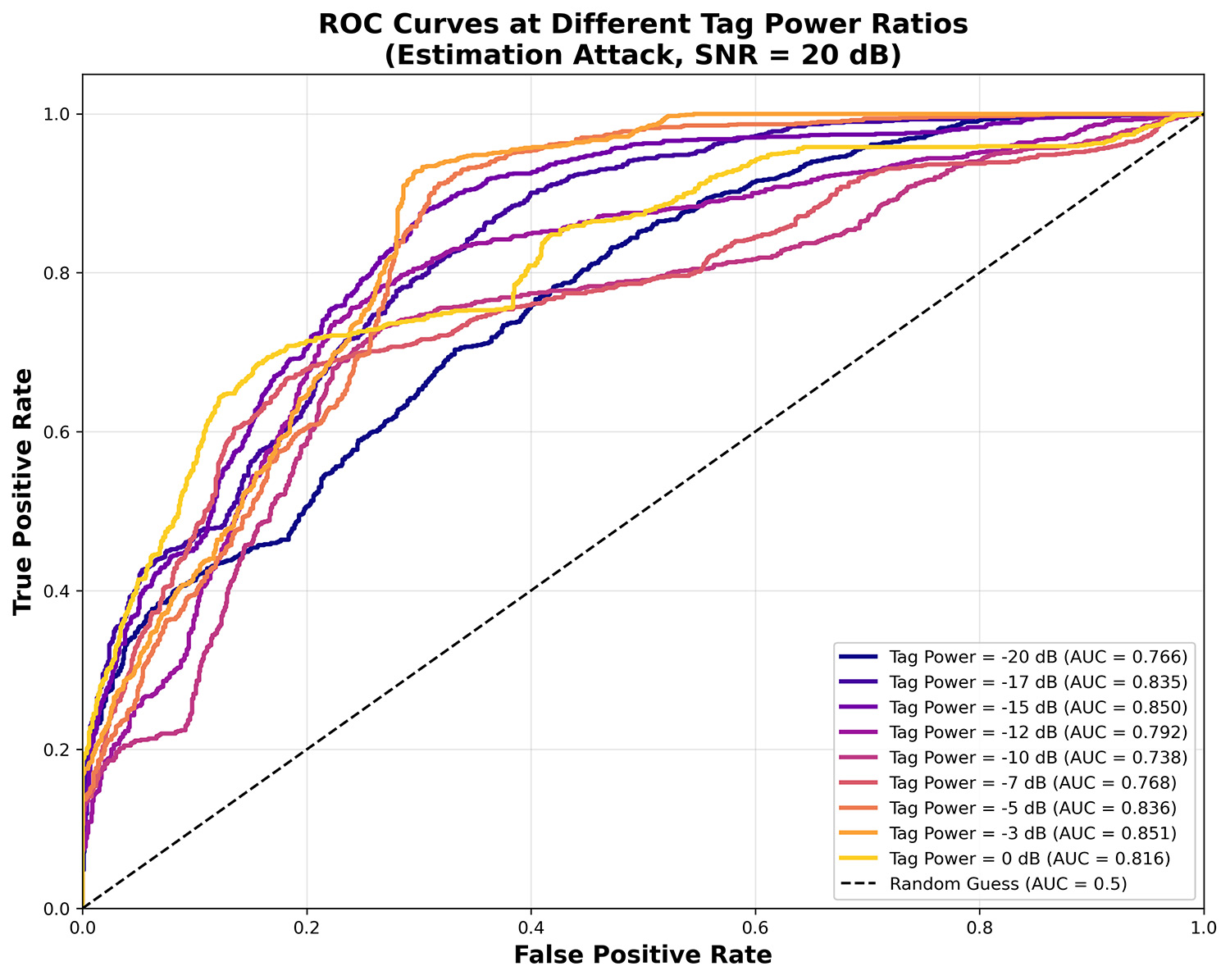
TY - JOUR AU - Salama, Amgad A. AU - Abdellatif, Ahmed Gamal AU - Safwat, Soha AU - Shah, Syed T. AU - Shawky, Mahmoud A. PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/09 TI - Constellation Warping-Based QAM Signal Watermarking for Secure and Reliable Wireless Communications JO - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography T2 - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography JF - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 29 EP - 42 DO - 10.62762/TISC.2025.407888 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.407888 KW - anti-spoofing KW - authentication KW - constellation warping KW - physical layer security KW - QAM KW - watermarking KW - wireless security AB - This paper investigates the performance of constellation warping techniques in QAM signals as a novel approach for physical layer authentication. We introduce a dynamic watermarking method that embeds subtle warping patterns into QAM constellations, enabling receivers to authenticate legitimate transmissions while detecting spoofing attacks. Our time-varying watermarking scheme employs secure key-based pattern generation to resist replay and estimation attacks. Extensive simulations analyze the system's resilience against various attack types (replay, blind spoofing, and estimation-based) across different signal-to-noise ratios. Results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves high detection rates ($>90%$ at moderate SNRs) with minimal false alarms and negligible impact on communication performance. We further identify optimal warping strengths and authentication thresholds that maximize security while minimizing symbol error rate degradation. The findings establish constellation warping as an effective physical layer security technique for wireless communications systems that face sophisticated spoofing threats. SN - 3070-2429 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Salama2026Constellat,
author = {Amgad A. Salama and Ahmed Gamal Abdellatif and Soha Safwat and Syed T. Shah and Mahmoud A. Shawky},
title = {Constellation Warping-Based QAM Signal Watermarking for Secure and Reliable Wireless Communications},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {29-42},
doi = {10.62762/TISC.2025.407888},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.407888},
abstract = {This paper investigates the performance of constellation warping techniques in QAM signals as a novel approach for physical layer authentication. We introduce a dynamic watermarking method that embeds subtle warping patterns into QAM constellations, enabling receivers to authenticate legitimate transmissions while detecting spoofing attacks. Our time-varying watermarking scheme employs secure key-based pattern generation to resist replay and estimation attacks. Extensive simulations analyze the system's resilience against various attack types (replay, blind spoofing, and estimation-based) across different signal-to-noise ratios. Results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves high detection rates (\$>90\%\$ at moderate SNRs) with minimal false alarms and negligible impact on communication performance. We further identify optimal warping strengths and authentication thresholds that maximize security while minimizing symbol error rate degradation. The findings establish constellation warping as an effective physical layer security technique for wireless communications systems that face sophisticated spoofing threats.},
keywords = {anti-spoofing, authentication, constellation warping, physical layer security, QAM, watermarking, wireless security},
issn = {3070-2429},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/