Abstract
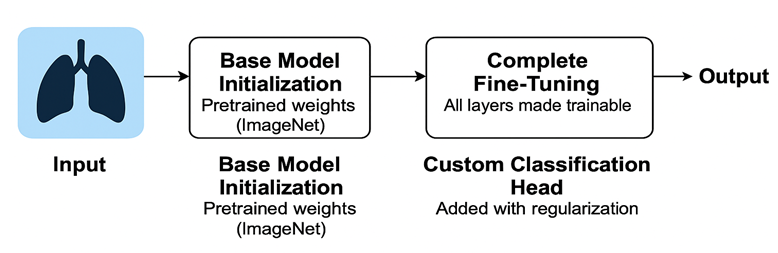
Lung cancer is predominantly illustrated as the principal cause of cancer-related deaths globally, especially the diagnosis of late stages creates substantial reductions in survival rate. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and medical imaging offer promising avenues for early and accurate detection of pulmonary malignancies. This paper introduces an EfficientNetB0 deep learning architecture used for performing multiclass lung cancer detection through computed tomography scan analysis. The EfficientNetB0 framework was validated, trained and tested on six clinically relevant CT scan image types within a publicly accessible Kaggle database. A combination of transfer learning with complete fine-tuning and customized classification head along with regularization enabled the model to reach a test accuracy of 83.58% macro-average AUC of 0.9492 and a weighted F1-score of 0.85. The testing results demonstrated excellent performance in malignant and normal classes, however have an insufficient ability to identify underrepresented benign cases due to class imbalance effects. This research includes visual diagrams of system architecture together with training performance graphs and a complete metric data examination. The achieved results elucidated EfficientNetB0 as an effective and lightweight backbone solution for computer-aided diagnosis systems used in pulmonary oncology.
Keywords
lung cancer
deep learning
convolutional neural networks
EfficientNetB0
medical image analysis
computed tomography
computer-aided diagnosis
transfer learning
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Khalid, H., Shahwaiz, A., & Zia, M. H. (2025). Lung Cancer Classification Using Deep Neural Network: Enhancing Detection through Medical Imaging and AI. ICCK Transactions on Radiology and Imaging, 1(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.62762/TRI.2025.492338
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue