Abstract
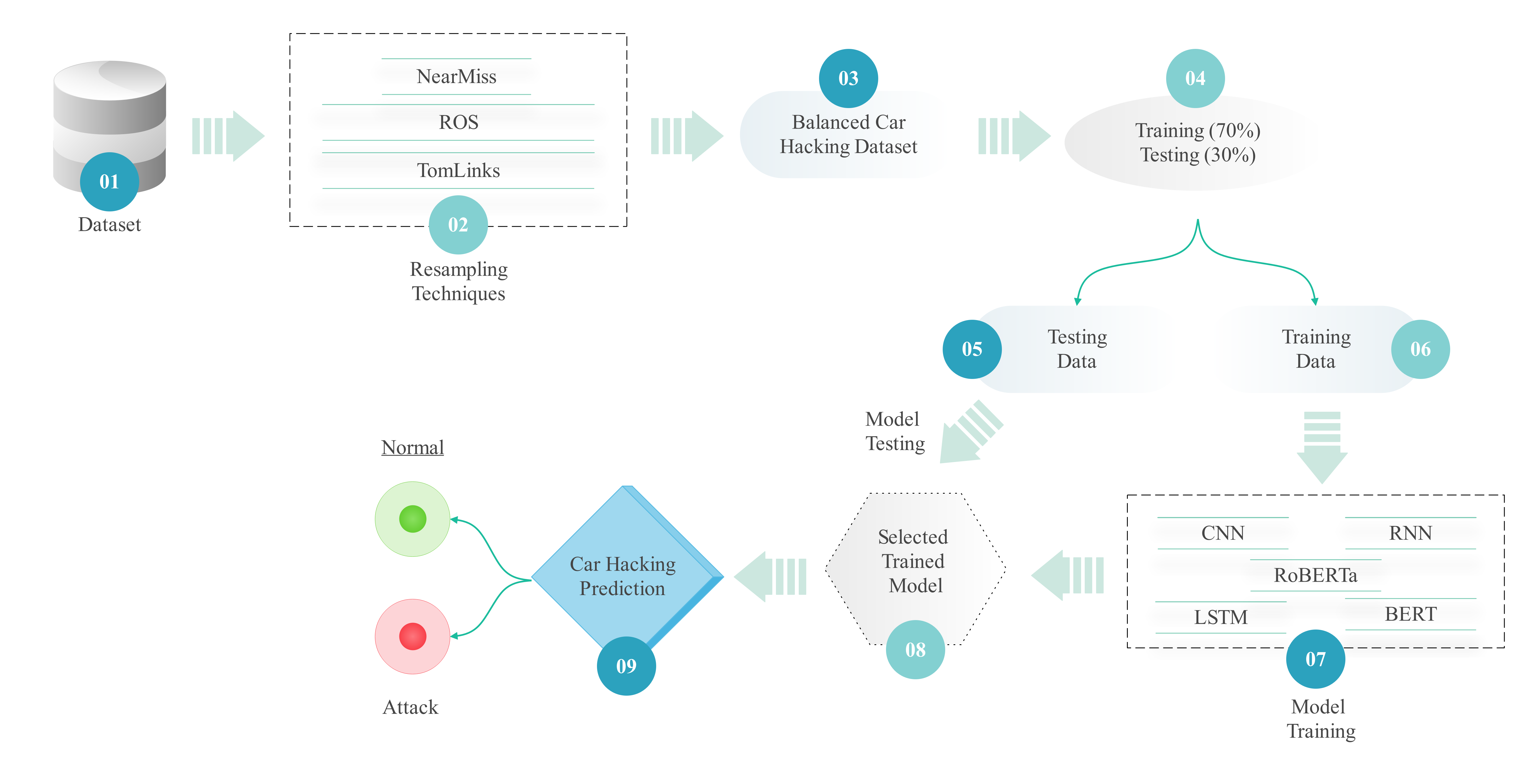
The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) has greatly influenced transportation by allowing autonomous vehicles to interact and communicate with other cars as well as with the surrounding traffic system. Even so, being interconnected comes with risks in terms of cyber attacks, for example, by injecting messages or fooling sensors through CAN systems. The study, consequently, suggests an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) that uses Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), and RoBERTa, to properly detect and handle these cyber threats. To solve the problem of unbalanced data, we use Random Over-Sampling (ROS), NearMiss, and Tomek Links, which makes the model work more effectively. Results from experiments show that the IDS suggested here is better than traditional machine learning models. Adopting cloud computing helps make the system more flexible and lets it be watched continually to keep AVs well protected. An IDS in smart cities greatly benefits vehicle networks, as it hinders and stops possible cyberattacks. Related work will aim to improve IDS performance for big organizations and cope with new types of attacks.
Keywords
autonomous vehicles (AVs)
cyber-attack detection
internet of vehicles (IoV)
bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT)
cybersecurity
smart cities
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Khan, F. M., Haider, Z. A., Khan, M. O., Ullah, A., Khan, M. S., Fayaz, M., Ahmad, M., & Nabila (2025). Intelligent Cyber-Attack Detection for Autonomous Vehicles Using Advanced Deep Learning Models. ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems, 2(2), 27–39. https://doi.org/10.62762/TACS.2025.952297
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
