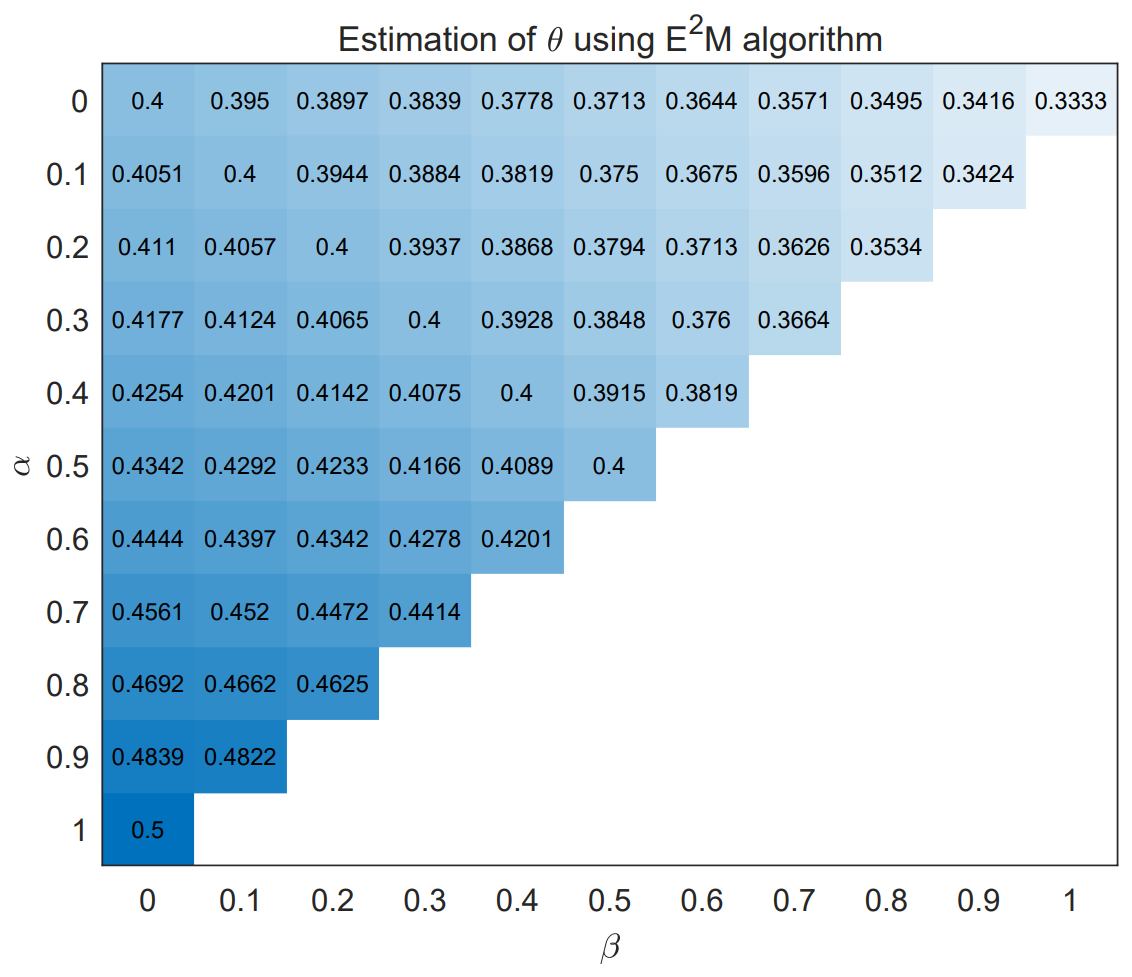
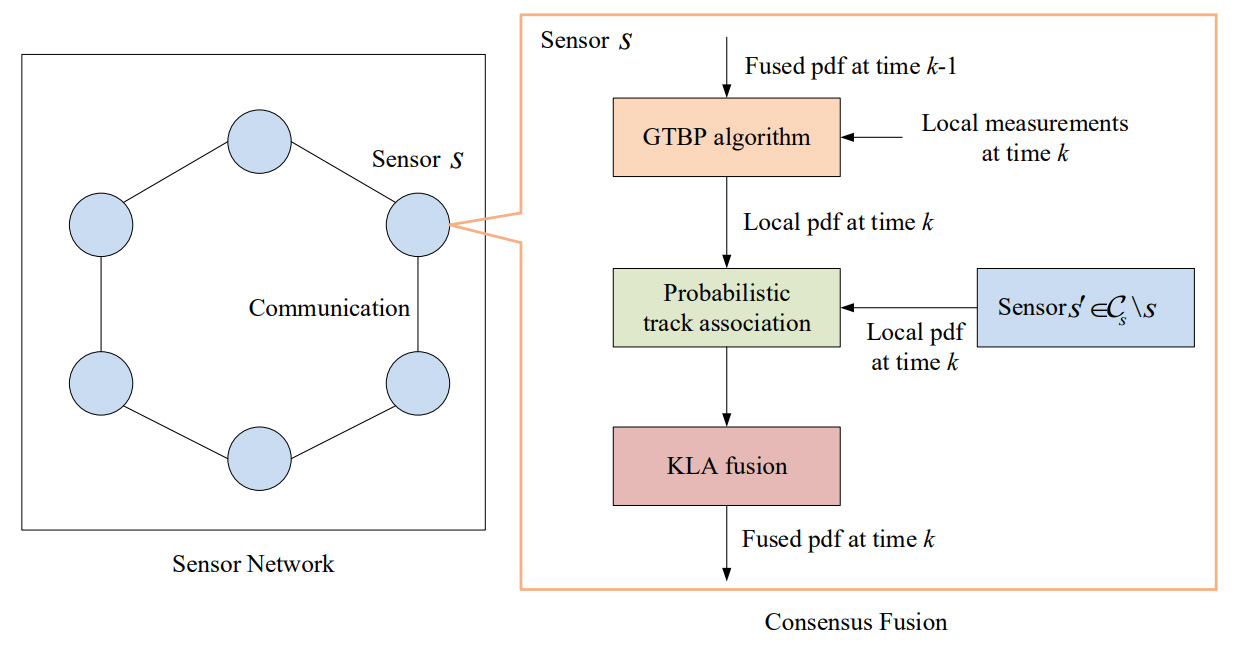
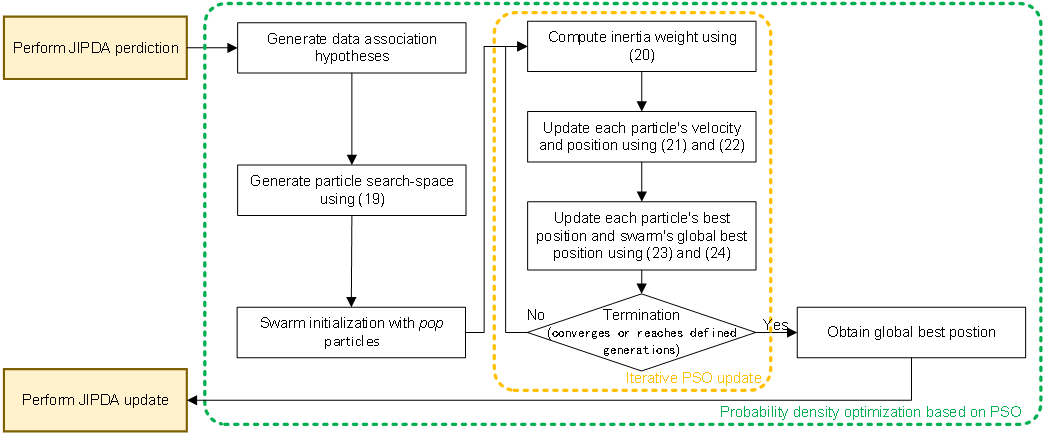
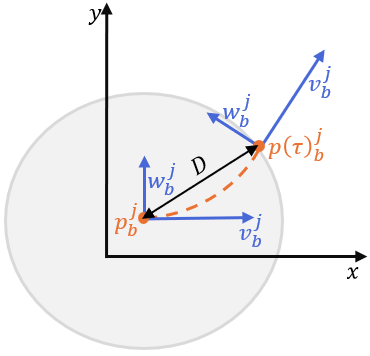
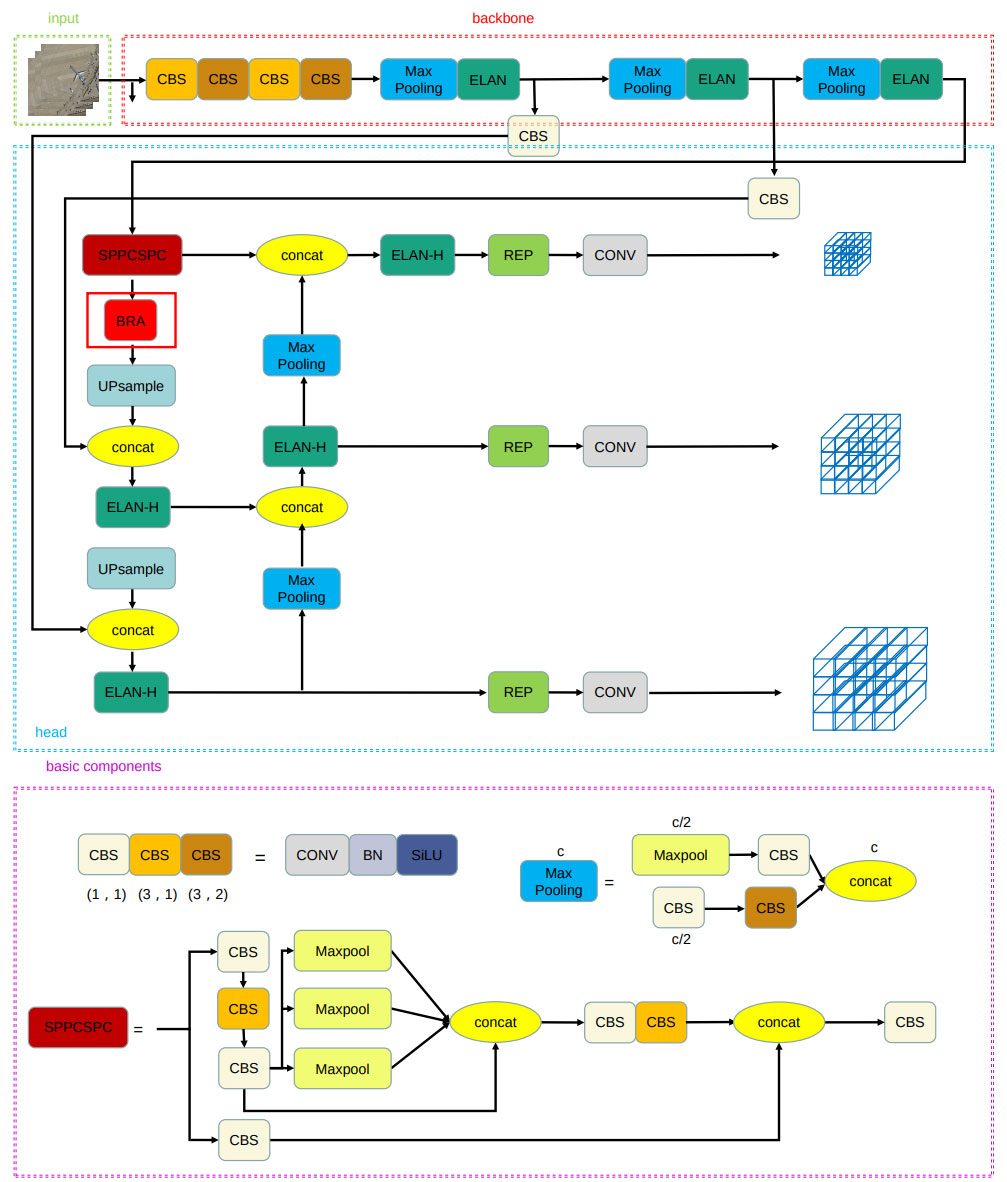
Chinese Journal of Information Fusion | Volume 3, Issue 1: 46-61, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/CJIF.2025.922221
Abstract
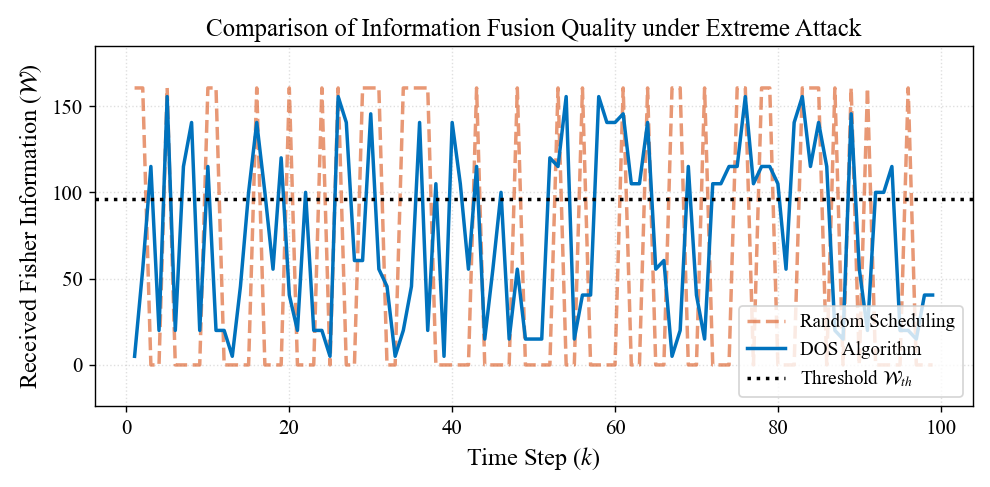
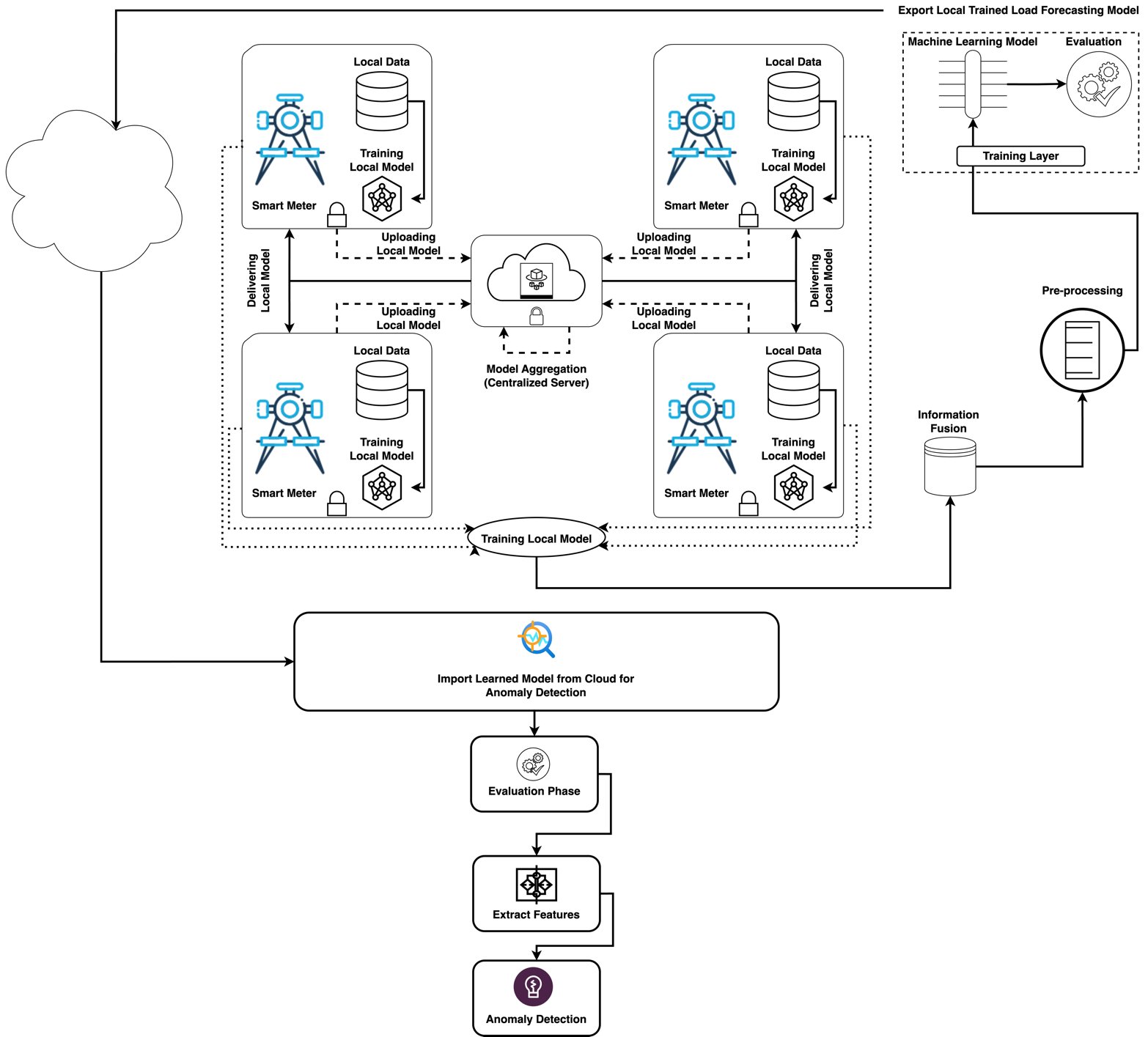
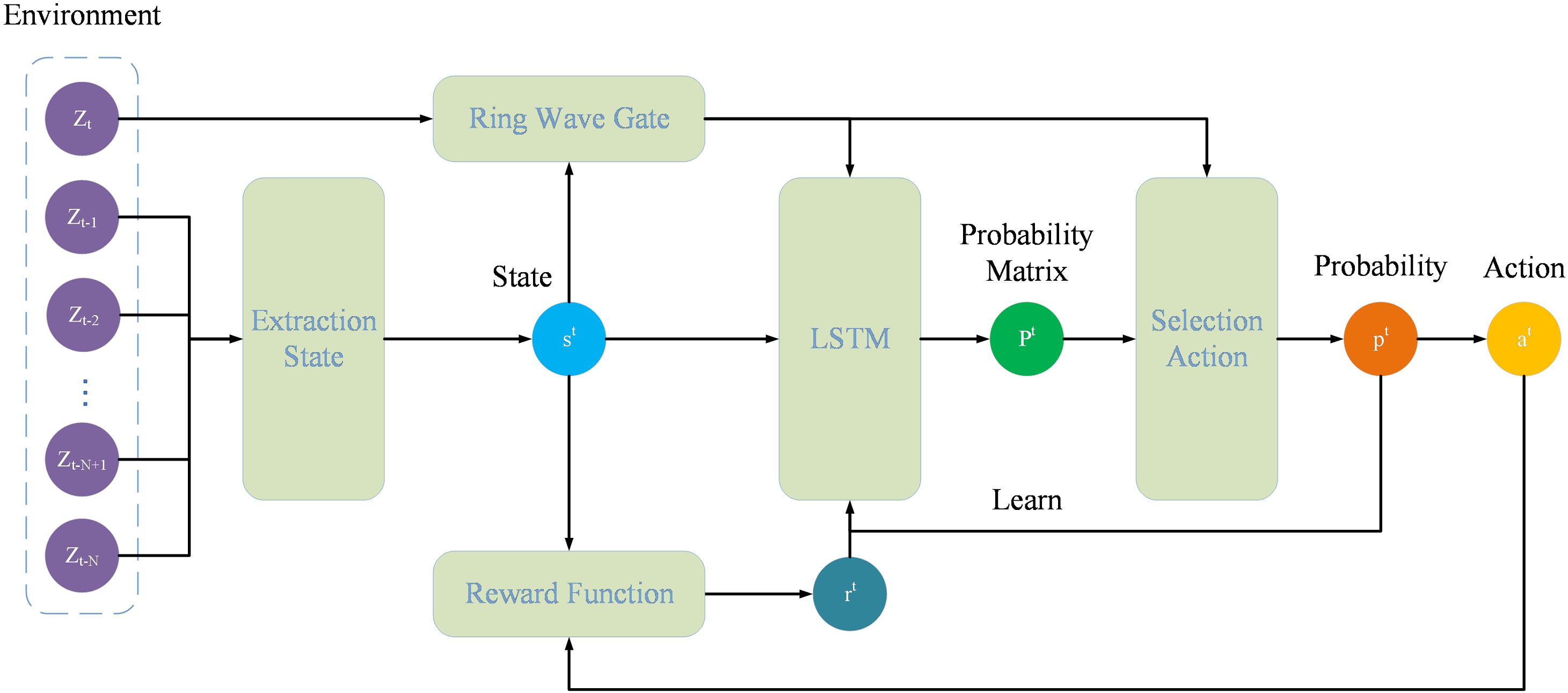
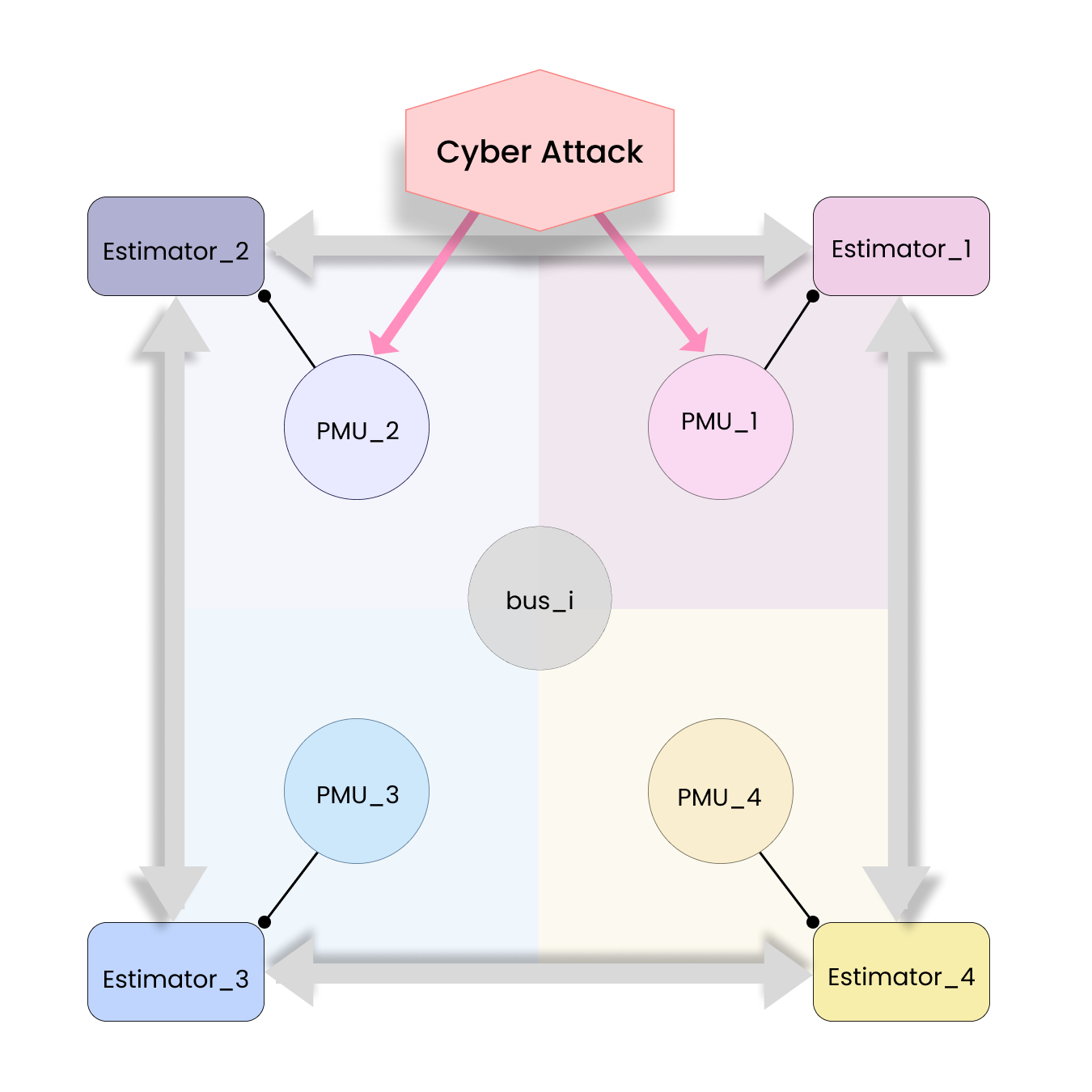
In this paper, we consider the state estimation problem in a cyber-physical system (CPS) against intermittent denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, which are usually difficult to defend due to their concealment and unpredictability. To address this issue, this paper proposes a dynamic observation scheduling method based on Fisher information to achieve efficient and resilient state estimation. Specifically, a sliding window mechanism is first employed to predict the successful transmission probability for each time window. Subsequently, the method constructs a scheduling sequence by aligning these predicted probabilities with the Fisher information of the observation's components. This strategy e... More >
Graphical Abstract